Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 33

Bent Toward Science: Refraction
Source Institutions
This is an activity about the behavior of light. Using simple, everyday objects, learners will discover that light moves in straight lines until acted upon by another object.
Triboluminescence
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover what happens when they crush wintergreen-flavored candies in a very dark room.

Two Lenses in One
Source Institutions
In this activity about light, learners explore how water can refract light and change the way they see things.

Give and Take
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore liquid crystals, light and temperature. Using a postcard made of temperature-sensitive liquid crystal material, learners monitor temperature changes.

Convection Current
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own heat waves in an aquarium.

Why is the Sky Blue?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a flashlight, a glass of water, and some milk to examine why the sky is blue and sunsets are red.

Soap Bubble Shapes
Source Institutions
Learners explore three-dimensional geometric frames including cubes and tetrahedrons, as they create bubble wands with pipe cleaners and drinking straws.
Liquid Crystals Interact with Light!
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity, learners explore the properties of liquid crystals, which are responsible for why mood rings change color.

Currently Working
Source Institutions
Learners test solutions of water, sugar, salt, and hydrochloric acid for electrical conductivity. They immerse leads from a lighting device (a battery pack connected to an LED) into each solution.

Light Soda
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners sublimate dry ice and then taste the carbon dioxide gas.

Water Illusions: Refraction & Magnification
Source Institutions
Learners demonstrate how water can distort, refract and magnify light.

Inverse Functions: Pennies, Pressure, Temperature, and Light
Source Institutions
The major goal of this math lesson is to have learners collect data from a variety of experiments, determine what models best fits their data, and explain why their models are best.
Dirty Oil, Oily Dirt
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how sediment is affected in an oil spill. Learners investigate the differences between heavy and light oil as well as the differences between different sediments.

Critical Angle
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners examine how a transparent material such as glass or water can actually reflect light better than any mirror.

Light as Air
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 6 of the PDF), learners will demonstrate air has weight by comparing an inflated balloon to a deflated one.
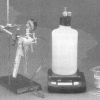
As Light as Air
Source Institutions
Learners measure a bottle full of air, and then use a vacuum pump to remove the air. When they re-weigh the bottle, learners find the mass is about 0.8g less.

Lighting Up Celery Stalks
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a series of hands-on experiments that demonstrate how the working of plants' veins, known as capillary action, enables water to travel throughout the length of a pla

Bubble Suspension
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe as soap bubbles float on a cushion of carbon dioxide gas. Learners blow bubbles into an aquarium filled with a slab of dry ice.

Changing Colors
Source Institutions
Learners experiment with a commercially available liquid-crystal coaster. They warm the material with their hands for varying lengths of time and observe the changing colors that result.
Water Wire: Electricity Flowing Through Water
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 10 of the PDF, learners detect the amount of energy that can flow through a sodium chloride electrolyte solution with a light sensor.
