Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 42
Water Treatment
Source Institutions
Water treatment on a large scale enables the supply of clean drinking water to communities.

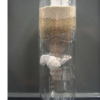
Disappearing Crystals
Source Institutions
Learners experiment with water gel crystals, or sodium polyacrylate crystals, which absorb hundreds of times their weight in water. When in pure water, the water gel crystals cannot be seen.

Stick to It: Adhesion II
Source Institutions
Water sticks to all kinds of things in nature — flowers, leaves, spider webs - and doesn't stick to others, such as a duck's back.

Build An Aqueduct
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use the design thinking process to design and build their own aqueduct, or water bridge.

Convection Current
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own heat waves in an aquarium.

PVC Water Squirter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a water squirter using a PVC pipe, dowel, and foam. This activity is great for the summer time and introduces learners to forces and water pressure.

Free-Fall Bottles & Tubes
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners conduct two experiments to explore free-falling.

Water Body Salinities II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss the different salinities of oceans, rivers and estuaries.

Freezing Lakes
Source Institutions
In some parts of the world, lakes freeze during winter. In this activity learners will explore water’s unique properties of freezing and melting, and how these relate to density and temperature.
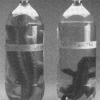
Crocodiles
Source Institutions
Learners observe and compare the sizes of three toy “growing” crocodiles made from water-absorbent polymers. One is it its original state, dry, hard, and about 10cm long.

Starch Slime
Source Institutions
Learners mix liquid water with solid cornstarch. They investigate the slime produced, which has properties of both a solid and a liquid.

Exploring Forces: Gravity
Source Institutions
In this nanoscience activity, learners discover that it's easy to pour water out of a regular-sized cup, but not out of a miniature cup.

Having a Gas with Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a simple electrolysis device. With this device, learners can decompose water into its elemental components: hydrogen and oxygen gas.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Nutrients in an Estuary
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model estuaries, artificially enriching both fresh and salt water samples with different amounts of nutrients and observing the growth of algae over several weeks.

Water Quality and pH Levels in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this fun and in depth hands-on experiment, learners test various liquid samples (distilled water, lemon juice, vinegar, and baking soda mixed with water) to determine their pH levels and identify e

Forwards and Backwards
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore acids and bases by preparing six solutions that combine vinegar and ammonia, ranging from acid (all vinegar) to base (all ammonia).

Got Gas?
Source Institutions
Create gas with a glass of water, some wire, conductors and a battery! You will be separating water (H2O) into oxygen and hydrogen.

Phase Changes
Source Institutions
Learners observe a sealed test tube containing a small amount of solid stearic acid.
Egg Osmosis
Source Institutions
Visitors observe three beakers. One beaker contains an egg immersed in vinegar. Visitors observe carbon dioxide gas escaping from the shell as the calcium carbonate reacts with the vinegar.
