Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 66
Water Motor
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 10 of the PDF), learners will explore how energy from moving water can be used.

Salt 'n Lighter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that as the salinity of water increases, the density increases as well. Learners prove this by attempting to float fresh eggs in saltwater and freshwater.

Build An Aqueduct
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use the design thinking process to design and build their own aqueduct, or water bridge.
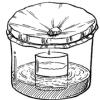
Rain Machine (Solar Still)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to build simple solar stills filled with salt water. After the stills are complete, learners observe what happens when they place the stills in the sun.

Exploring Size: Ball Sorter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use sieves with different-sized holes to sort balls by size.

Pop Can "Hero Engine"
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build water-propelled engines from soft drink cans.

Magic Sand: Nanosurfaces
Source Institutions
This is an activity/demo in which learners are exposed to the difference bewteen hydrophobic surfaces (water repelling) and hydrophilic surfaces (water loving).

Exploring Forces: Gravity
Source Institutions
In this nanoscience activity, learners discover that it's easy to pour water out of a regular-sized cup, but not out of a miniature cup.
Ships Ahoy!
Source Institutions
Design a vessel that tests the limits of wind power given a set of off the shelf and recycled materials.

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.
It's A Gas!
Source Institutions
Visitors mix water and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) in a large flask. They then add citric acid to the mixture and stopper the flask. The resulting reaction creates carbon dioxide gas.

Diving Submarine
Source Institutions
Learners use a commercially available toy to experiment with density. They fill a chamber in the toy submarine with baking powder and release it into a tank of water.

Static Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use static elecricity to bend a stream of water without touching it. Learners will explore physics and cause and effect through this activity.

Draggin' Boats
Source Institutions
Learners design, build, and test models of "dragon boats" made from up to three milk cartons.
Finding the Right Crater
Source Institutions
This quick demonstration (on page 11 of PDF) allows learners to understand why scientists think water ice could remain frozen in always-dark craters at the poles of the Moon.

Exploring Products: Nano Sand
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how water behaves differently when it comes in contact with "nano sand" and regular sand.
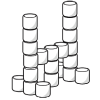
Marshmallow Models
Source Institutions
No glue is needed for learners of any age to become marshmallow architects or engineers.
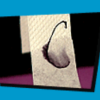
Chromatography
Source Institutions
In this activity, explore chromatography and the various colors that make up the ink in markers. Use this activity to investigate cohesion and adhesion.

Does Size Make a Difference?
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 15 of the PDF, discover how materials and physical forces behave differently at the nanoscale.

Exploring Materials: Hydrogel
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how a super-absorbing material can be used to move a straw.
