Search Results
Showing results 1 to 11 of 11

Water Engineering
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will engineer a water irrigation system. Learners will create a ditch irrigation system -- or an acequia-- to move water with the help of gravity.

Water Cycle in a Bag
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore the water cycle by creating a small atmosphere.
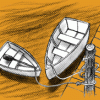
Watercraft
Source Institutions
In this design challenge activity, learners build a boat that can hold 25 pennies (or 15 one inch metal washers) for at least ten seconds before sinking.

Model Well
Source Institutions
In this quick activity about pollutants and groundwater (page 2 of PDF under Water Clean-up Activity), learners build a model well with a toilet paper tube.
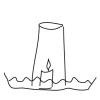
Thirsty Candle
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore the dynamics of air pressure by using a candle, a cup, and a dish of water.
Up, Up and Away with Bottles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make water rockets to explore Newton's Third Law of Motion. Learners make the rockets out of plastic bottles and use a bicycle pump to pump them with air.
Finding the Right Crater
Source Institutions
This quick demonstration (on page 11 of PDF) allows learners to understand why scientists think water ice could remain frozen in always-dark craters at the poles of the Moon.

Ocean Currents
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore how density is affected by temperature and how that can create currents.
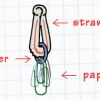
Deep Sea Diver
Source Institutions
In this ocean engineering activity, learners explore buoyancy and water displacement. Then, learners design models of deep sea divers that are neutrally buoyant.

Hydraulic Car
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build cars using syringes and water-powered hydraulics. Learners construct the car frame out of cardboard and set up a hydraulic system to raise and lower the car.

Earth Atmosphere Composition
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use rice grains to model the composition of the atmosphere of the Earth today and in 1880. Learners assemble the model while measuring percentages.
