Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 95

Free-Fall Bottles & Tubes
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners conduct two experiments to explore free-falling.

Water Body Salinities II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss the different salinities of oceans, rivers and estuaries.
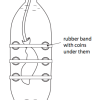
Submersibles and Marshmallows
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the difficulty of ocean exploration by human beings as they investigate water pressure.

Science at the Waterpark!
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Water Slides) is a full inquiry investigation into speed and motion and takes place at a water park.

Lighting Up Celery Stalks
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a series of hands-on experiments that demonstrate how the working of plants' veins, known as capillary action, enables water to travel throughout the length of a pla

Forces at the Nanoscale: Nano Properties of Everyday Plants
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of PDF under Nasturtium Leaves Activity) about surface tension.

Freezing Lakes
Source Institutions
In some parts of the world, lakes freeze during winter. In this activity learners will explore water’s unique properties of freezing and melting, and how these relate to density and temperature.
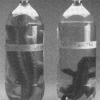
Crocodiles
Source Institutions
Learners observe and compare the sizes of three toy “growing” crocodiles made from water-absorbent polymers. One is it its original state, dry, hard, and about 10cm long.

Wet Art
Source Institutions
In this activity (located on page 10 of the PDF), learners explore the properties of spraying and dripping water, while making art.
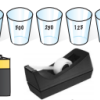
Water Wire: Electricity Flowing Through Water
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 10 of the PDF, learners detect the amount of energy that can flow through a sodium chloride electrolyte solution with a light sensor.

School of Fish
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make fish cutouts that propel through the water with the help of surface tension.

Starch Slime
Source Institutions
Learners mix liquid water with solid cornstarch. They investigate the slime produced, which has properties of both a solid and a liquid.

Exploring Forces: Gravity
Source Institutions
In this nanoscience activity, learners discover that it's easy to pour water out of a regular-sized cup, but not out of a miniature cup.

The Liquid Rainbow
Source Institutions
Learners are challenged to discover the relative densities of colored liquids to create a rainbow pattern in a test tube.

Moving Without Wheels
In a class demonstration, learners observe a simple water cycle model to better understand its role in pollutant transport.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Having a Gas with Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a simple electrolysis device. With this device, learners can decompose water into its elemental components: hydrogen and oxygen gas.

Fragile Waters
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 18-29) learners explore the impact of the March 24, 1989 oil spill in Alaska caused by the Exxon Valdez tanker.

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.

Boats Afloat
Source Institutions
In this water activity, learners build boats that float and sink. First, learners listen to the book, "Who Sank the Boat" and practice making predictions throughout the story.
