Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 48

Heat Capacity: Can't Take the Heat?
Source Institutions
Why is ocean water sometimes the warmest when the average daily air temperature starts to drop? In this activity, learners explore the differing heat capacities of water and air using real data.

Make a Water Cycle Wristband
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners thread colored beads onto string. Each beach represent a process of the water cycle.

Solar Water Heater
Learners work in teams to design and build solar water heating devices that mimic those used in residences to capture energy in the form of solar radiation and convert it to thermal energy.

Cool It!
Source Institutions
Learners make a refrigerator that works without electricity. The pot-in-pot refrigerator works by evaporation: a layer of sand is placed between two terra cotta pots and thoroughly soaked with water.

The Rain Man
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the hydrologic cycle in action as water evaporates and condenses to form rain right before their eyes.

Do Sweat It!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore why humans sweat. Learners compare the effects of heat on a balloon filled with air and a balloon filled water.

Leaf it to Me
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the effect of transpiration as water is moved from the ground to the atmosphere.

From Gas to Liquid to Solid
Source Institutions
What causes frost to form on the outside of a cold container? In this activity, learners discover that liquid water can change states and freeze to become ice.
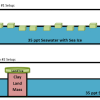
Causes and Effects of Melting Ice
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the concept of density-driven currents (thermohaline circulation) and how these currents are affected by climate change.

Solar Convection
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners add food coloring to hot and cold water in order to see how fluids at different temperatures move around in convection currents.

Evaporation
Source Institutions
This three-part activity consists of an activity that groups of learners develop themselves, a given procedure, and an optional demonstration.

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.
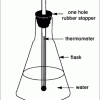
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Can Crushers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment by heating an aluminum can filled with water to investigate air pressure.

Meltdown
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners heat ice and water of the same temperature to get a hands-on look at phase changes. This is an easy and inexpensive way to introduce states of matter and thermodynamics.

Thermal Energy Put to Work
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners determine whether thermal energy can be used for work.

Condensation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the process of condensation.

Hot and Cold
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore temperature changes from chemical reactions by mixing urea with water in one flask and mixing calcium chloride with water in another flask.

Energetic Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how hot and cold water move. Learners observe that temperature and density affect how liquids rise and fall.
