Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 37
Space Stations: Bones of Contention
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make models representing bones on Earth and bones that have been in space. They discover what happens to bones without proper exercise and nutrition.

Dry Ice Comet
Source Institutions
In this activity, dry ice and other items are used to construct a demonstration model of a comet that illustrates the comet nucleus, coma, and tails.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Solar System Bead Distance
Source Institutions
In this astronomy activity, learners create a model of the solar system using beads and string.
Mars from Above: Carving Channels
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create channel features with flowing water, comparing their observations to real images of Mars and Earth taken by satellites/orbiters.

Infant Moon: Moon Mix!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the Moon's infancy and model how an ocean of molten rock (magma) helped shape the Moon that we see today.
Recipe for a Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the Moon, like Earth, is made up of layers of different materials. Learners work in teams to make models of the interiors of the Moon and Earth.

Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets
Source Institutions
In "Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets," participants learn about how some rockets carry science tools—not scientists—into space, and how a special kind of rocket called "sounding rockets" can
Solar System in My Neighborhood
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners shrink the scale of the vast solar system to the size of their neighborhood.

Mars from Above: Viewing Volcanoes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create volcanoes like those they have examined on Earth and Mars through images taken by spacecraft.

Gravity and Falling
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners experiment with a bucket, stretchy fabric, marbles, and weights to discover some basics about gravity.
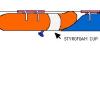
Balloon Staging
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate a multistage rocket launch using party balloons, fishing line, straws, and a plastic cup.

Exploring the Universe: Nebula Spin Art
Source Institutions
In this activity, participants will learn about how gigantic clouds of gas and dust in space, called nebulas, are formed. They'll create their own colorful model nebula using paint and a spinner.

Weather Stations: Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test how cornstarch and glitter in water move when disturbed. Learners compare their observations with videos of Jupiter's and Earth's storm movements.
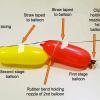
Achieving Orbit
Source Institutions
In this Engineering Design Challenge activity, learners will use balloons to investigate how a multi-stage rocket, like that used in the Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) mission, can propel a sat

Investigating the Insides
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in teams to investigate the composition of unseen materials using a variety of tools.

Teen Moon: Moon Ooze
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model how the Moon's volcanic period reshaped its earlier features.
