Search Results
Showing results 1 to 10 of 10

Dry Ice Comet
Source Institutions
In this activity, dry ice and other items are used to construct a demonstration model of a comet that illustrates the comet nucleus, coma, and tails.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Searching for Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss how life is defined and conduct a simple experiment, looking for signs of life in three different “soil” samples.
Space Stations: Measure Up!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in pairs to measure each other's ankles with lengths of string.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

Cooling Off
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are introduced to challenges of maintaining temperatures while living in space.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.
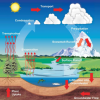
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

Aerogel-lo
Source Institutions
This demonstration (on pages 9-11) uses gelatin and lead pellets to model how aerogel, a technology used by NASA spacecrafts, is used to capture comet particles.
