Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 24

False Memories
Source Institutions
Use this activity (10th on the page) to help learners explore memory and how sometimes your brain makes up its own memories. Learners will read and try to remember the words in list #1.

Sock It To Me!
Source Institutions
In this activity (7th activity on the page), learners use their sense of touch to identify mystery objects hidden in socks.

Half Full or Half Empty
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th activity on the page), learners conduct an experiment to demonstrate how muscles are constantly feeding information to the brain about what they are doing.

Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that it is difficult to trace a curve by using its reflection in a mirror. Use this activity to discuss how the brain works.

Molecule Match
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use their nose to sniff out hidden scents using extracts and cotton balls. Activity includes materials list, game instructions, STEM connections and more.

Shrinking Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners control the (apparent) size of a hole with their brain.
Smell Detective
Source Institutions
In this activity about olfaction (8th activity on the page), learners smell 10 different items with different odors. Then they try to identify the smells when they are mixed together.

Edible/Inedible
Source Institutions
In this activity about olfaction (9th activity on the page), learners smell 10 different items with different odors, including some edible food items.
Become a Neurologist: Detective Threshold
Source Institutions
In this neuroscience activity (4th activity on the page), learners make their own set of Von Frey hairs to test detection thresholds.

Memory Solitaire
Source Institutions
In this online game, learners practice memory recall. They are shown a collage of pictures for two minutes, then have to write down everything they remember and check how they did.
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.
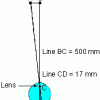
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.

Sand Paper Rankings
Source Institutions
In this activity (2nd activity on the page), learners explore the sensitivity of their sense of touch.

How Sweet It Is
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners use their sense of smell to rate and arrange containers filled with different dilutions of a scent (like cologne or fruit juice) in order from wea

No Saliva, No Taste?
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners test to see if saliva is necessary for food to have taste.
Why Are Two Eyes Better Than One?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how their depth perception would be affected if they only had one eye. Learners work in pairs and attempt to drop a penny in a cup with one eye covered.

Head, Shoulder, Knees and Toes...and Hands, Fingers and Back
Source Institutions
Are fingers the only place on the body where we use our sense of touch? In this activity (6th activity on the page), learners test the touch sensitivity of different parts of the body.

See It to Believe It: Visual Discrimination
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th on the page), learners investigate their ability to discriminate (see) different colors.

Active Touch
Source Institutions
In this activity (14th activity on the page) about the sense of touch, learners examine if it is easier or harder to identify an object if they move their hands over it.
