Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 22

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 3
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the human influences on the carbon cycle and examine how fossil fuels release carbon.

Carbon Sequestration
Source Institutions
In this inquiry-based lesson, learners measure the biomass of trees, calculate the carbon stored by the trees, and use this information to create recommendations about using trees for carbon sequestra

The Carbon Cycle Game
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take on the role of a carbon atom and record which reservoirs in the carbon cycle they visit.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 2
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 7), learners explore the meaning of a "carbon sink." Using simple props, learners and/or an educator demonstrate how plants act as carbon sinks and how greenhouse gases cause

Dinosaur Breath
Through discussion and hands-on experimentation, learners examine the geological (ancient) carbon cycle.
The Carbon Cycle: Carbon Tracker
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners play NOAA's Carbon Tracker game and discover ways to keep track of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the world.

Corals and Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate how increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the burning of fossil fuels is changing the acidity (pH) of the ocean and affecting coral reefs and other marin

Automotive Emissions and the Greenhouse Effect
Source Institutions
In this activity about global climate change, learners will conduct an experiment and collect data to compare the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in four different sources of gases.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 1
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 1), learners role play as atoms to explore how atoms can be rearranged to make different materials.

A Dissolving Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners add objects and substances to carbonated water to discover that added objects increase the rate at which dissolved gas comes out of solution.

Off Base
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the factors that tend to resist changes in pH of the ocean and why the ocean is becoming more acidic.

Introduction to the Scientific Method
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 26 of the PDF), learners make observations, formulate hypotheses and design a controlled experiment, based on the reaction of carbon dioxide with calcium hydroxide.

Shell Shifts
Source Institutions
Ocean acidification is a big issue due to the amount of carbon dioxide humans release. CO2 in the atmosphere is absorbed into the ocean thus changing its acidity.

Fill 'er Up!
Source Institutions
Learners discover that their breath contains carbon dioxide, one of the pollutants found in car exhaust.
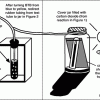
How Greenhouse Gases Absorb Heat
Source Institutions
Learners observe two model atmospheres -- one with normal atmospheric composition and another with an elevated concentration of carbon dioxide.
Yeast Balloons
Source Institutions
Visitors observe a bottle with a balloon attached around the mouth. The bottle contains a solution of yeast, sugar, and water.

Film Canister Rocket
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct and launch rockets using simple materials and their understanding of chemical reactions.

The Effects of Acid Rain
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity (page 4 of the PDF), learners use vinegar and chalk to observe the effect of acid rain on various building materials and plant life.
It's A Gas!
Source Institutions
Visitors mix water and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) in a large flask. They then add citric acid to the mixture and stopper the flask. The resulting reaction creates carbon dioxide gas.
