Search Results
Showing results 121 to 140 of 202

M&M's in Different Temperatures
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to investigate whether the temperature of the surrounding water affects the rate at which the colored coating dissolves from an M&M.
Chew that Gum
Source Institutions
In this quick activity (page 1 of PDF under SciGirls Activity: Exercise and Memory), learners will investigate what happens to bubble gum when it is chewed for 5-10 minutes.

A Recipe for Air
Learners use M&Ms® (or any other multi-color, equally-sized small candy or pieces) to create a pie graph that expresses the composition of air.

Solar Convection
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners add food coloring to hot and cold water in order to see how fluids at different temperatures move around in convection currents.
How Does Water Climb a Tree?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to explore how water flows up from a tree's roots to its leafy crown.

Ziptop Bag Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this chemistry activity, learners perform three chemical reactions in a sealed zip-top bag. Learners will record their observations and classify the changes as chemical or physical.

What's in the Water?: Biotic and Abiotic Elements in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this investigation learners explore the differences between, and interdependence of, living and nonliving elements in a water ecosystem.
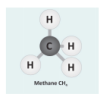
Let's Make Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use gumdrops and toothpicks to model the composition and molecular structure of three greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4).

M&M's in Different Sugar Solutions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate whether having sugar already dissolved in water affects the speed of dissolving and the movement of sugar and color through the water.

Cool It!
Source Institutions
In this fun hands-on activity, learners use simple materials to investigate evaporation. How can the evaporation of water on a hot day be used to cool an object? Find out the experimental way!
Everyday Poisons
Source Institutions
This reading and writing activity (on pages 2-9) teaches what plant parts should be avoided, how a person can get rid of toxins, symptoms of plant poisoning, and how plants create poisons to repel pre

Soda Geyser
Source Institutions
In this quick activity (page 1 of PDF under SciGirls Activity: Lift Off), learners will use the ever-popular soda geyser experiment to test the reactivity of the various sugar candies or mints.

Milk Plastic
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners transform everyday milk into small plastic figurines and jewelry. Use this activity to introduce learners to monomers and polymers.

Nuclear Fusion
Source Institutions
This simple and engaging astronomy activity explains nuclear fusion and how radiation is generated by stars, using marshmallows as a model.

Model Well
Source Institutions
In this quick activity about pollutants and groundwater (page 2 of PDF under Water Clean-up Activity), learners build a model well with a toilet paper tube.
Dinosaur Bone Experiments
Source Institutions
This activity features two connected hands-on activities about dinosaur bones.
Spaghetti Bridge
Source Institutions
Play with your food while learning about engineering! Build a spaghetti bridge, then test its strength by piling on the marshmallows, raw spaghetti, raw linguine and coins.

Egg Osmosis: A four day eggsperience!
Source Institutions
Eggs are placed in vinegar for one or two days to dissolve the shells. Then, learners place the eggs in water or corn syrup and observe them over a period of days.

Yeast Balloons: Can biochemistry blow up a balloon?
Source Institutions
Using yeast, sugar, and water, learners create a chemical reaction which produces carbon dioxide (CO2) gas inside a 2-liter bottle. They use this gas to inflate a balloon.

Diet Light
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how the added sugar in a can of soda affects its density and thus, its ability to float in water.
