Search Results
Showing results 1 to 12 of 12
Light Bulb Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the difference between compact fluorescent light (CFL) bulbs and traditional incandescent bulbs.

The Geophysical Light/Dark Cycle
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 131 of the PDF) related to sleep and circadian rhythms as well as space travel.

Transit Tracks
Source Institutions
In this space science activity, learners explore transits and the conditions when a transit may be seen.
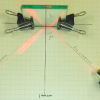
Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test the Law of Reflection based on experimental evidence. Learners produce raw data and explanations based on their data: pencil tracings of incident and reflection rays.

Super Sleuths
Source Institutions
In this physical sciences activity, learners use science to solve a "crime." Learners collect trace evidence (glitter) and explore its characteristics, such as color, size, shape, and light reflection

The Senses of "Unknown Creatures"
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use earthworms as "unknown creatures" from the South American jungle to find out how animals use senses.

How Our Environment Affects Color Vision
Source Institutions
In this lab (Activity #1 on page), learners explore how we see color.
Multiple Reflections
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how mirrors reflect light and change the way we see things.

Hot Air
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners set up an experiment to investigate the effects of hot air on the path of a laser beam.

Can Energy be Created or Destroyed?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore conservation of energy by experimenting with a solar cell light device.
Tools of Magnification
Source Institutions
In this activity related to microbes, learners use water drops and hand lenses to begin the exploration of magnification. This activity also introduces learners to the microscope.
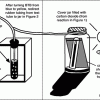
How Greenhouse Gases Absorb Heat
Source Institutions
Learners observe two model atmospheres -- one with normal atmospheric composition and another with an elevated concentration of carbon dioxide.
