Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 35
Effects of Solar Radiation on Land and Sea
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the different heating properties of soil and water.
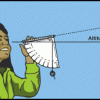
Using a Simple Astrolabe
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use an astrolabe to measure the altitude of objects. Learners will first practice taking measurements by measuring the altitude of trees and buildings.

Measure the Sun's Size
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own pinhole viewer in order to measure the size of the sun.

Measuring Earthquakes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build their your own seismograph with household materials to document shaking.
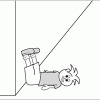
Space Stations: Measure Up!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in pairs to measure each other's ankles with lengths of string.
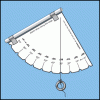
Making a Simple Astrolabe
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make an astrolabe, a device used for measuring altitude, including the height of objects in the sky.

Height Sight
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a tool called an inclinometer that can find the height of any distant object, from a tree to the North Star.

Balloon Impacts
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure the diameter of their water balloons, model an impact, measure the diameter of the “crater” area, and determine the ratio of impactor to crater.

Measure the Speed of a Water Leak
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 2 of PDF under GPS: Glaciers Activity), learners will measure the rate at which water streams out of a leaky cup.

Map That Habitat
Source Institutions
Historically, sea floor mapping (bathymetry) was done by soundings.

Does Air Weigh Anything?
Source Institutions
The demonstration/experiment provides quick proof that air has mass.
Light on Other Planets
Source Institutions
In this math-based activity, learners model the intensity of light at various distances from a light source, and understand how astronomers measure the amount of sunlight that hits our planet and othe

Turbidity
Source Institutions
This is an activity about turbidity, or the amount of sediment suspended in water.

Measure the Pressure II: The "Dry" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.

Toast a Mole!
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners drink Avogadro's number worth of molecules - 6.02x10^23 molecules!
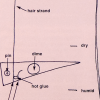
Better Hair Through Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners hook up a hair to a lever system and create a hair hygrometer to measure changes in humidity.

Sizing Up Hail
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will estimate the sizes of balls to learn how to estimate the size of hail. Learners will compare their estimates to the estimates of their peers and the real measurements.

Meteoroids and the Craters They Make
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the formation of craters. Learners will examine how the size, angle and speed of a meteorite's impact affects the properties of craters.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

