Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 23
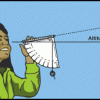
Using a Simple Astrolabe
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use an astrolabe to measure the altitude of objects. Learners will first practice taking measurements by measuring the altitude of trees and buildings.

The Shadow Knows I
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of their shadow from the Sun and compare it three to four months later.
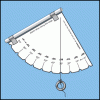
Making a Simple Astrolabe
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make an astrolabe, a device used for measuring altitude, including the height of objects in the sky.

Exploring Earth: Temperature Mapping
Source Institutions
This activity models the way Landsat satellites use a thermal infrared sensor to measure land surface temperatures.

Experiencing Parallax With Your Thumb
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate parallax, a method used to measure distances to stars and planets in the solar system.

Turbidity
Source Institutions
This is an activity about turbidity, or the amount of sediment suspended in water.
Globe at Night
Source Institutions
In this international citizen science activity, learners measure their night sky brightness and submit their observations into an online database.
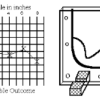
Topographic Investigation: Map an Underwater Surface
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a map of a hidden surface using a "sounding stick" -- a technique similar to how underwater maps were once made.

It's the "Rain," Man
Source Institutions
In this weather forecasting activity, learners use common materials to construct a rain gauge and measure daily, monthly, and yearly rainfall.
The Size and Distance of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the concepts of relative size and distance by creating a basic model of the solar system.

Sizing Up Hail
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will estimate the sizes of balls to learn how to estimate the size of hail. Learners will compare their estimates to the estimates of their peers and the real measurements.

Big Sun, Small Moon
Source Institutions
Learners will explore the concept of angular distance, and investigate why the moon appears to be the same size as the sun during a solar eclipse, despite the sun being much larger.

Meteoroids and the Craters They Make
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the formation of craters. Learners will examine how the size, angle and speed of a meteorite's impact affects the properties of craters.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

Exploring the Solar System: Moonquakes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners sort different natural phenomena into categories (they occur on Earth, on the Moon, or on both), and then model how energy moves during a quake using spring toys.

Pocket Solar System: Make a Scale Model
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners build a scale model of the universe with little more than adding machine tape.

Canned Heat
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how light and dark colored objects absorb the Sun's radiations at different rates.

Shaking It!
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners design and build a model room in a shoebox and furnish it with tiny furniture.

Leaf it to Me
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the effect of transpiration as water is moved from the ground to the atmosphere.

Ancient Sun Observations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own Sun tracker to explore how ancient civilizations around the world studied the Sun.
