Search Results
Showing results 61 to 80 of 124

Jump to Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners help create and then navigate an outdoor course of the traditional "planets" (including dwarf planet Pluto), which are represented by small common objects.

Exploring the Solar System: Moonquakes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners sort different natural phenomena into categories (they occur on Earth, on the Moon, or on both), and then model how energy moves during a quake using spring toys.

What Causes Pressure?
Source Institutions
In this kinesthetic activity that demonstrates pressure, learners act as air molecules in a "container" as defined by a rope.
Percentage of Oxygen in the Air
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere by using steel wool's ability to rust.

Relative Speed of Dinosaurs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners interpret three trackways and use measurements and a formula to infer the relative speed of dinosaurs.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Mold Mole Molds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make different shapes that hold exactly one mole of gas (air).

Earth Atmosphere Composition
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use rice grains to model the composition of the atmosphere of the Earth today and in 1880. Learners assemble the model while measuring percentages.

Our Solar System to Scale
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners plan and create a 24-foot long, two-dimensional model of our solar system, and compare and contrast the differences between planets and the sun.

Pocket Solar System: Make a Scale Model
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners build a scale model of the universe with little more than adding machine tape.
Twirling in the Breeze
Source Institutions
In this engineering activity, learners build a device (an anemometer) to measure how fast the wind is blowing.

Atmosphere Composition Model
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a model using metric measuring tapes and atmosphere composition data.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Make a Prism
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make their own prism and use a glass of water to separate sunlight into different colors.
Crater Maker
In this activity (on pages 6-11), learners work as a team to investigate how impact craters on Earth, the Moon or other planets take shape and what patterns they make.

Going Green
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a waste audit and use their findings to implement a plan for reducing trash.

Build a Solar System
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a scale model of the Solar System and learn the real definition of "space." Learners use the online calculator to create an appropriate scale to use as a basis for thei
Investigating Density Currents
Source Institutions
In this lab activity, learners explore how to initiate a density current. Learners measure six flasks with different concentrations of salt and water (colored blue).
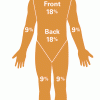
Measuring and Protecting Skin
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners compare and contrast their own skin (including the area covered) with that of an orange.

Breathing Blue
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test exhaled breath for carbon dioxide and learn how to use an indicator as a simple way to measure pH.
