Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 66
Making Rivers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor water activity, learners explore how to change the direction of water flow. Learners make puddles in dirt or use existing puddles and sticks to make water flow.

Detect Solar Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build their own magnetometer using an empty soda bottle, magnets, laser pointer, and household objects.

Toast a Mole!
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners drink Avogadro's number worth of molecules - 6.02x10^23 molecules!

The Ability of Permeability
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 11 of the PDF), learners investigate how quickly water moves through various materials. They measure and compare the permeability of gravel, sand, and soil.

Glaciers
Source Institutions
In this online activity, learners adjust mountain snowfall and temperature to see how glaciers grow and shrink. They will use scientific tools to measure thickness, velocity and glacial budget.

Big Sun, Small Moon
Source Institutions
Learners will explore the concept of angular distance, and investigate why the moon appears to be the same size as the sun during a solar eclipse, despite the sun being much larger.

Meteoroids and the Craters They Make
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the formation of craters. Learners will examine how the size, angle and speed of a meteorite's impact affects the properties of craters.

What Causes Pressure?
Source Institutions
In this kinesthetic activity that demonstrates pressure, learners act as air molecules in a "container" as defined by a rope.
Percentage of Oxygen in the Air
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere by using steel wool's ability to rust.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Mold Mole Molds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make different shapes that hold exactly one mole of gas (air).

Earth Atmosphere Composition
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use rice grains to model the composition of the atmosphere of the Earth today and in 1880. Learners assemble the model while measuring percentages.

Atmosphere Composition Model
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a model using metric measuring tapes and atmosphere composition data.

Make a Prism
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make their own prism and use a glass of water to separate sunlight into different colors.
Crater Maker
In this activity (on pages 6-11), learners work as a team to investigate how impact craters on Earth, the Moon or other planets take shape and what patterns they make.
Investigating Density Currents
Source Institutions
In this lab activity, learners explore how to initiate a density current. Learners measure six flasks with different concentrations of salt and water (colored blue).
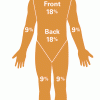
Measuring and Protecting Skin
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners compare and contrast their own skin (including the area covered) with that of an orange.

Breathing Blue
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test exhaled breath for carbon dioxide and learn how to use an indicator as a simple way to measure pH.

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.

