Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 34

Do Plants Need Sunlight?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners find out what happens when they cover leaves with pieces of black construction paper. This activity shows learners that plants need sunlight to survive.

How Plants Grow
Source Institutions
In this biology activity (page 3 of the PDF), learners will explore how plants turn sunlight into food through a process called photosynthesis.
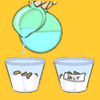
Salt, Soil and Seeds
Source Institutions
Discover how the salt in soil affects plant growth with a few seeds, some cotton, and salt. In this hands-on activity, you will plant seeds in 2 different kinds of soil, containing more or less salt.
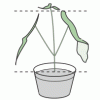
Do Plants Need Light?
Source Institutions
In this food science activity, learners conduct an experiment that demonstrates the importance of light to plants.

Photosynthesis and Transpiration
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 7 of the PDF (Plants—The Green Machines), learners examine the effects that light and air have on green plants.

Mighty Seeds
Source Institutions
In this biology experiment, learners plant soybean seeds in plaster of Paris, witnessing firsthand the mighty power and ability of plants to grow in adverse conditions.

Growing Food From Scraps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore vegetative propagation while preparing food scraps to grow into plants.
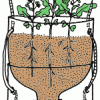
TerrAqua Investigation Column: What is the Land-Water Connection?
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners plant seeds in a 2-liter bottle filled with soil that is connected to a water source below. Over the next few weeks, learners observe how the plants grow.

What's Hiding in the Air?: Acid Rain Activity
As a model of acid rain, learners water plants with three different solutions: water only, vinegar only, vinegar-water mixture.

Moving On Up: Capillary Action 1
Source Institutions
Over the course of several days, learners explore the property of water that helps plants move water from roots to leaves or gives paper towels the capacity to soak up water.

Paper Chromatography with Leaves
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 5 of the PDF (Plants—The Green Machines), learners use chromatography to separate and identify pigments within various leaves.

Sand, Plants and Pants
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how the application of nano-sized particles or coatings can change a bigger material’s properties.

Super Soil
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners make their own organic-rich soil. Depending on where this activity is done, learners will probably discover that their local soil is low in organic matter.

Animal & Plant Cell Slides
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make slides of onion cells and their own cheek cells. Use this lab to teach learners how to prepare microscope slides and use a microscope.

Plant Power
Source Institutions
In this chemistry challenge, learners identify which plants have the enzyme "catalase" that breaks hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.

Moisture Makers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners compare the moisture released from different kinds of leaves and from different parts of the same leaf, by observing the color change of cobalt chloride paper.

Seeds: Roots and Shoots
Source Institutions
In this indepth hands-on activity, learners build a structure that allows them to observe the growth of roots and the correlation between root growth and stem extension.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 2
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 7), learners explore the meaning of a "carbon sink." Using simple props, learners and/or an educator demonstrate how plants act as carbon sinks and how greenhouse gases cause

Estuaries
Source Institutions
An estuary is a body of water that is created when freshwater from rivers and streams flows into the saltwater of an ocean.

Color-Changing Carnations
Source Institutions
Learners place cut flowers in colored water and observe how the flowers change. The flowers absorb the water through the stem and leaves.
