Search Results
Showing results 41 to 60 of 171

Build A Bee Bath
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use found natural materials to create a water haven for bees and other insects.
Ships Ahoy!
Source Institutions
Design a vessel that tests the limits of wind power given a set of off the shelf and recycled materials.

What's Hiding in the Air?: Acid Rain Activity
As a model of acid rain, learners water plants with three different solutions: water only, vinegar only, vinegar-water mixture.

Moving Without Wheels
In a class demonstration, learners observe a simple water cycle model to better understand its role in pollutant transport.

Convection Demonstration
Source Institutions
In this quick activity (located on page 2 of the PDF under GPS: Balloon Fiesta Activity), learners will see the effects of convection and understand what makes hot air balloons rise.

Fragile Waters
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 18-29) learners explore the impact of the March 24, 1989 oil spill in Alaska caused by the Exxon Valdez tanker.

OBIS Oil Spill
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners simulate an oil spill using popcorn (both oil and popcorn float on water), and estimate the spill's impact on the environment.
Up, Up and Away with Bottles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make water rockets to explore Newton's Third Law of Motion. Learners make the rockets out of plastic bottles and use a bicycle pump to pump them with air.
It's A Gas!
Source Institutions
Visitors mix water and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) in a large flask. They then add citric acid to the mixture and stopper the flask. The resulting reaction creates carbon dioxide gas.

Diving Submarine
Source Institutions
Learners use a commercially available toy to experiment with density. They fill a chamber in the toy submarine with baking powder and release it into a tank of water.

Gravity Fountains
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Glaciers Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into the forces of gravity and air pressure.

Static Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use static elecricity to bend a stream of water without touching it. Learners will explore physics and cause and effect through this activity.
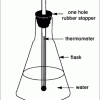
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Draggin' Boats
Source Institutions
Learners design, build, and test models of "dragon boats" made from up to three milk cartons.

Irrigation Ideas
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how civil engineers solved the challenge of moving water via irrigation.
Finding the Right Crater
Source Institutions
This quick demonstration (on page 11 of PDF) allows learners to understand why scientists think water ice could remain frozen in always-dark craters at the poles of the Moon.

Exploring Products: Nano Sand
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how water behaves differently when it comes in contact with "nano sand" and regular sand.
Marshmallow Models
Source Institutions
No glue is needed for learners of any age to become marshmallow architects or engineers.

Measure the Pressure: The "Wet" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.

The Best Dam Simulation Ever
Source Institutions
This online simulation game explores the different consequences of water levels on the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest.
