Search Results
Showing results 1 to 17 of 17

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.
Big and Little Cups
Source Institutions
In this indoor or outdoor water activity, learners pour water from small cups to large cups and containers. In doing so, they discover water takes the shape of its container.

Sink or Float?
Source Institutions
In this water activity, learners test which objects float and which sink. Learners discover that objects behave differently in water.
Float or Sink?
Source Institutions
In this water activity, learners test which objects float and which sink. Learners discover that objects behave differently in water.

Racing M&M Colors
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to determine which M&M color dissolves the fastest in water.

Slowing the Flow
Source Institutions
In this experiment, pairs of learners explore how cold water affects circulation. The mammalian diving reflex (MDR) slows circulation when the body is exposed to cold water.
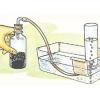
Pneumatic Trough
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a "pneumatic trough," a laboratory apparatus used for collecting pure gas samples over water.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Drying It Out
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate and compare the rate of drying in different conditions.

We all Scream for Ice Cream
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe how salinity affects the freezing point of water by making and enjoying ice cream.

Traveling Through Different Liquids
Source Institutions
Learners observe and record what happens when they manipulate bottles containing a liquid (water or corn syrup) and one or more objects (screw, nail, paper clip).

Dripping Wet or Dry as a Bone?
Learners investigate the concept of humidity by using a dry and wet sponge as a model. They determine a model for 100% humidity, a sponge saturated with water.
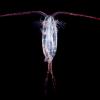
Plankton Feeding
Source Institutions
This activity provides a hands-on experience with a scale model, a relatively high viscosity fluid, and feeding behaviors.

Comparing the Density of Different Liquids
Source Institutions
Learners carefully pour vegetable oil, water, and corn syrup in any order into a cup and discover that regardless of the order they are poured, the liquids arrange themselves in layers the same way.

Digit's Cyber-Dough
Source Institutions
In this fun hands-on activity, learners whip up a batch of cyber-dough (play dough) using math for measurements.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Chromatography Can Separate!
Source Institutions
In this chemistry activity, learners use thin layer chromatography to determine the molecular composition of different markers.
