Search Results
Showing results 41 to 60 of 175

From Gas to Liquid to Solid
Source Institutions
What causes frost to form on the outside of a cold container? In this activity, learners discover that liquid water can change states and freeze to become ice.

Lighting Up Celery Stalks
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a series of hands-on experiments that demonstrate how the working of plants' veins, known as capillary action, enables water to travel throughout the length of a pla

Forces at the Nanoscale: Nano Properties of Everyday Plants
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of PDF under Nasturtium Leaves Activity) about surface tension.

Magic Sand: Nanosurfaces
Source Institutions
This is an activity/demo in which learners are exposed to the difference bewteen hydrophobic surfaces (water repelling) and hydrophilic surfaces (water loving).

Breathing Yeasties
Source Institutions
Does yeast breathe? Find out by watching how plastic bags filled with yeast, warm water and different amounts of sugar change over time.
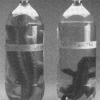
Crocodiles
Source Institutions
Learners observe and compare the sizes of three toy “growing” crocodiles made from water-absorbent polymers. One is it its original state, dry, hard, and about 10cm long.
Pollution in Our Watershed
Source Institutions
By building a simple watershed with paper and markers and then using a spray bottle to simulate precipitation, learners will understand how pollution accumulates in our water sources, especially from

School of Fish
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make fish cutouts that propel through the water with the help of surface tension.

Outrageous Ooze: Is It a Liquid or a Solid?
Source Institutions
This activity provides instructions for using cornstarch and water to make an ooze which has the properties of both a solid and liquid.

Starch Slime
Source Institutions
Learners mix liquid water with solid cornstarch. They investigate the slime produced, which has properties of both a solid and a liquid.

Make a UV Detector
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use tonic water to detect ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun and explore the concept of fluorescence.

Iron in the Environment
Source Institutions
In this chemistry activity (on page 2 of the PDF), learners corrode a penny in a cup with vinegar, salt water, and a source of iron (nails, paper clips, or twist ties).
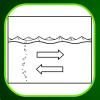
Current Events
Source Institutions
Learners model the ocean currents that carry hot water from the tropics to northern latitudes.
Up and Over
Source Institutions
This is an activity about Newton's First Law of Motion - a body in motion tends to stay in motion, or a body at rest tends to stay at rest unless acted upon by an outside force.

Egg Osmosis: A four day eggsperience!
Source Institutions
Eggs are placed in vinegar for one or two days to dissolve the shells. Then, learners place the eggs in water or corn syrup and observe them over a period of days.

Evaporation
Source Institutions
This three-part activity consists of an activity that groups of learners develop themselves, a given procedure, and an optional demonstration.

Moving Without Wheels
In a class demonstration, learners observe a simple water cycle model to better understand its role in pollutant transport.

Racing M&M Colors
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to determine which M&M color dissolves the fastest in water.

Convection Demonstration
Source Institutions
In this quick activity (located on page 2 of the PDF under GPS: Balloon Fiesta Activity), learners will see the effects of convection and understand what makes hot air balloons rise.

Collect Invertebrates to Determine Water Quality
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Alligator Habitat Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into organisms and the health of their ecosystems.
