Search Results
Showing results 121 to 140 of 381

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.

Oh Buoy!
Source Institutions
Learners work in pairs to design, construct, and test a device that exhibits positive, neutral, and negative buoyancy. They test a number of different objects in water to see if they sink or float.

Diving Submarine
Source Institutions
Learners use a commercially available toy to experiment with density. They fill a chamber in the toy submarine with baking powder and release it into a tank of water.

Handwashing Laboratory Activities: Bowl Technique
Source Institutions
In this lab (Activity #2 on page), learners compare bacteria growth on two petri dishes containing nutrient agar. Learners touch the doors, faucets, etc.

Gravity Fountains
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Glaciers Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into the forces of gravity and air pressure.

Oh Boy Buoyancy
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners will explore the concept of buoyancy, especially as it relates to density.

"Can" You Stand the Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity about states of matter, learners get to witness firsthand the awesome power of air pressure. They watch as an ordinary soda can is crushed by invisible forces.
The Water (Hydrologic) Cycle: Transpiration
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners grow broad bean (also called fava bean) plants in three EarthBoxes for a few weeks before exposing one to wind (using a fan), another to heat (using a lamp), and the third to not
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Echolocation Lab
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners experience how dolphins and other echolocating animals use their senses to locate and identify objects without using their sense of sight.
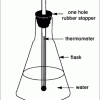
Pneumatic Trough
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a "pneumatic trough," a laboratory apparatus used for collecting pure gas samples over water.

Can Crushers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment by heating an aluminum can filled with water to investigate air pressure.

The Ability of Permeability
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 11 of the PDF), learners investigate how quickly water moves through various materials. They measure and compare the permeability of gravel, sand, and soil.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Inflate-a-mole
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find the volume of one mole of gas. Learners capture sublimated gas from dry ice in a ziploc bag and use water displacement to measure its volume.
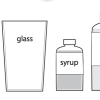
Density Stackers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate density as they discover how liquids separate to form density layers. Learners discover what happens when they add syrup, cooking oil, and water to a jar.

Exploring Moisture on the Outside of a Cold Cup
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the relationship between cooling water vapor and condensation. Learners investigate condensation forming on the outside of a cold cup.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Runaway Runoff
Source Institutions
When it rains, water can collect on top of and seep into the ground. Water can also run downhill, carrying soil and pollution with it.
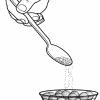
Inner Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that there is space between molecules even in a cup "full" of water. They first fill a cup with marbles, and then add sand to fill the gaps between the marbles.
