Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 66
The Daily Ups and Downs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners graph 48 hourly air temperatures from a local weather observation site and observe the diurnal temperature variations.
Forward Thinking
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create their own weather forecast map.
Weathering and Erosion
Source Institutions
In this multi-station lab, learners conduct a series of experiments to explore the processes and effects of weathering and erosion.

Weather Vane
Source Institutions
In this meteorology activity, learners build weather vanes using straws, paperclips, and cardstock.

Weather and Climate: What's the Difference?
Source Institutions
This lesson plan enables learners to explore the differences between weather and climate.

If Anyone Can, Icon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create their own icons for a forecast-at-a-glance poster for their classroom/learning space.

What's the Difference between Weather and Climate?
Source Institutions
In this interactive and informative group activity, learners use packages of M&M's to illustrate the difference between weather and climate.

Sizing Up Hail
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will estimate the sizes of balls to learn how to estimate the size of hail. Learners will compare their estimates to the estimates of their peers and the real measurements.
Updrafts in Action
Source Institutions
In this weather activity/demonstration, learners watch as a ping pong ball is suspended in a stream of air supplied by a hair dryer.

Rocking Changes
Source Institutions
In this earth science activity, learners conduct a series of short experiments to explore how rocks change.
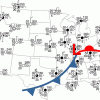
Drawing Conclusions
Source Institutions
In this weather forecasting activity, learners determine the location of cold and warm fronts on weather plot maps.

Weather Vane and Anemometer
Source Institutions
In this meteorology activity, learners construct simple devices to measure the direction and speed of wind.

Gravestone Weathering
Source Institutions
In this activity (located on pages 9-14 of PDF), learners visit a cemetery to examine the distinguishing characteristics of rock weathering.
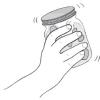
Shake and Break
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will model the mechanical weathering and erosion of rocks in a stream or river.

How Boulders Are Born
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners review and discuss weathering, erosion and mass wasting, to gain a stronger understanding of how Hickory Run’s Boulder Field was formed after the Laurentide Continental Glac

Weather Stations: Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test how cornstarch and glitter in water move when disturbed. Learners compare their observations with videos of Jupiter's and Earth's storm movements.

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.

Do Cities Affect the Weather?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore clouds and how they form.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Space Weather Action Center
Source Institutions
In this interdisciplinary activity, learners create a Space Weather Action Center (SWAC) to monitor solar storms and develop real SWAC news reports.
