Search Results
Showing results 1 to 17 of 17

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Measure the Pressure: The "Wet" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.

Measure the Pressure II: The "Dry" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.
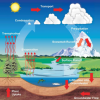
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

Inverted Bottles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate convection by using food coloring and water of different temperatures.

How Much Water is in that Cloud?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners working in pairs saturate a cotton ball using water drops from an eyedropper to demonstrate the high water capacity of clouds.

Fog Chamber
Source Institutions
In this weather-related activity, learners make a portable cloud in a bottle.

What is a “Convection Cell”?
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners can observe a number of small convection cells generated from a mixture of aluminum powder and silicon oil on a hot plate.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

Turning the Air Upside Down: Spinning Snakes
Learners color and cut out a spiral-shaped snake. When they hang their snake over a radiator, the snake spins.
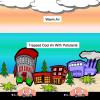
Turning the Air Upside Down: Convection Current Model
Learners see convection currents in action in this highly visual demonstration. Sealed bags of colored hot or cold water are immersed in tanks of water.

Turning the Air Upside Down: Warm Air is Less Dense than Cool Air
Learners cover a bottle with a balloon. When they immerse the bottle in warm water, the balloon inflates. When they immerse the bottle in a bowl of ice, the balloon deflates.

Diet Light
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how the added sugar in a can of soda affects its density and thus, its ability to float in water.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

We all Scream for Ice Cream
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe how salinity affects the freezing point of water by making and enjoying ice cream.

I Can't Take the Pressure!
Learners develop an understanding of air pressure in two different activities.
