Search Results
Showing results 41 to 60 of 172

Parabolas: It's All Done with Mirrors
Source Institutions
In this activity about light and reflection, learners use a special device called a Mirage Maker™ to create an illusion.

See the World Through Color-Filtering Lenses
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners examine how colored lenses act like filters and absorb all colors of light except for the color of the lenses.

Pinhole Magnifier
Source Institutions
In this activity related to light and perception, learners use a pinhole in an index card as a magnifying glass to help their eye focus on a nearby object.

Paper Lanterns
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore light and shadows by creating a lantern they can keep on their nightstand.

Give and Take
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore liquid crystals, light and temperature. Using a postcard made of temperature-sensitive liquid crystal material, learners monitor temperature changes.

Shadow Puppets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will create their own simple shadow puppets, and experiment with light and shadow while playing with them.

Self-Portrait Silhouettes: Activity 1
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a photographic image--without a camera!

Bike Wheel Zoetrope
Source Institutions
In this activity (posted on April 18, 2011), learners follow the steps to construct a zoetrope, a device that produces an illusion of action from a rapid succession of static pictures, using a 16" bik
Stretch the Chain and See the Light
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use their strength to light a light bulb. A chain made from paper clips is placed in series with a battery and flashlight bulb.

Luminescence
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity about luminescence, learners explore the chemistry that happens inside glow sticks and other light producing reactions.
Sliding Gray Step
Source Institutions
How can you make one shade of gray look like two? By putting it against two different color backgrounds! This activity allows learners to perform this sleight of hand very easily.
Slide Projector Activities
Source Institutions
This resource contains several mini-explorations using a slide projector as a light source to investigate light and the properties of images.

It's all Done with Mirrors
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity illustrates the path of light as it reflects off of mirrors and how this is used in telescopes.
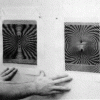
Moiré Patterns
Source Institutions
In this activity about light and perception, learners create and observe moire patterns.
The Primary Colors of Light
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups of four to explore light. Learners create new colors from the primary colors of light from flashlights covered in theatrical gels or cellophane.
Illuminating Luminescence
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners compare and contrast different forms of luminescence by observing how chemiluminescence, phosphorescence, and fluorescence produce or emit light.

Stroboscope
Source Institutions
In this activity (posted on March 20, 2011), learners follow the steps to construct a stroboscope, a device that exploits the persistence of vision to make moving objects appear slow or stationary.
Multiple Reflections
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how mirrors reflect light and change the way we see things.

Polarized Light Mosaic
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use transparent tape and polarizing material to create and project beautifully colored patterns reminiscent of abstract or geometric stained glass windows--no glass required

CD Spectrometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a compact disc to make a spectrometer, an instrument used to measure properties of light.
