Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 41

Acid (and Base) Rainbows
Learners use red cabbage juice and pH indicator paper to test the acidity and basicity of household materials. The activity links this concept of acids and bases to acid rain and other pollutants.

Invisible Ink Demonstration
Source Institutions
In this chemistry demonstration, learners will discover that phenolphthalein is a chemical that displays different colors depending on the acidity or basicity of the environment.
Forwards and Backwards: pH and Indicators
Source Institutions
Visitors prepare six solutions combining vinegar and ammonia that range incrementally from acid (all vinegar) to base (all ammonia).

Jell-O Model of Microfluidics
Source Institutions
This activity uses Jell-O(R) to introduce learners to microfluidics, the flow of fluids through microscopic channels.

Acid Rain Effects
Learners conduct a simple experiment to model and explore the harmful effects of acid rain (vinegar) on living (green leaf and eggshell) and non-living (paper clip) objects.
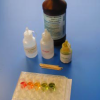
Finding Colors
Source Institutions
In this chemistry challenge, learners combine acids and bases in a universal indicator to create five different colors.

The Colors of Flowers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment to find out what determines a flower's color.

What's In Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test to see if carbon dioxide is present in the air we breathe in and out by using a detector made from red cabbage.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Hot Stuff!: Testing for Carbon Dioxide from Our Own Breath
Learners blow into balloons and collect their breath--carbon dioxide gas (CO2). They then blow the CO2 from the balloon into a solution of acid-base indicator.
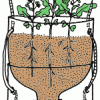
TerrAqua Investigation Column: What is the Land-Water Connection?
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners plant seeds in a 2-liter bottle filled with soil that is connected to a water source below. Over the next few weeks, learners observe how the plants grow.
Of Cabbages and Kings
Source Institutions
This lesson gives full instructions for making cabbage juice indicator, a procedure sheet for learners to record observations as they use the indicator to test materials, and extension activities to d

Fruit Juice Mystery
Source Institutions
In this chemistry challenge, learners work to figure out which of four juices are real, and which is just food coloring and sugar.

Breathing Blue
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test exhaled breath for carbon dioxide and learn how to use an indicator as a simple way to measure pH.

Hot Stuff!: Creating and Testing for Carbon Dioxide
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda reacting to form carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
Electrolysis is the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen. This Exploratorium activity allows learners to visualize the process with an acid-based indicator.

Hot Stuff!: Testing Ice
In this demonstration, learners compare and contrast regular water ice to dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide). Both samples are placed in a solution of acid-base indicator.

Kimchee Fermentation Chamber
Source Institutions
Learners make kimchee or sauerkraut, which is really just fermented cabbage, in a 2-liter plastic bottle.

Corals and Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate how increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the burning of fossil fuels is changing the acidity (pH) of the ocean and affecting coral reefs and other marin

Forwards and Backwards
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore acids and bases by preparing six solutions that combine vinegar and ammonia, ranging from acid (all vinegar) to base (all ammonia).
