Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 88

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #4
Learners test two jars containing soil, one covered and one open, for changes in temperature. After placing the jars in the Sun, learners discover that the covered jar cools down more slowly.

Dripping Wet or Dry as a Bone?
Learners investigate the concept of humidity by using a dry and wet sponge as a model. They determine a model for 100% humidity, a sponge saturated with water.

Acid (and Base) Rainbows
Learners use red cabbage juice and pH indicator paper to test the acidity and basicity of household materials. The activity links this concept of acids and bases to acid rain and other pollutants.

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #1
Learners test two jars, one containing plain air and one containing carbon dioxide gas, to see their reactions to temperature changes.

How Can Gravity Make Something Go Up?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cheap, thin plastic garbage bags to quickly build a solar hot air balloon. In doing so, learners will explore why hot air rises.

Good News: We're on the Rise!
Learners build a simple aneroid barometer to learn about changes in barometric pressure and weather forecasting. They observe their barometer and record data over a period of days.

Acid Rain Effects
Learners conduct a simple experiment to model and explore the harmful effects of acid rain (vinegar) on living (green leaf and eggshell) and non-living (paper clip) objects.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

What's Hiding in the Air?: Acid Rain Activity
As a model of acid rain, learners water plants with three different solutions: water only, vinegar only, vinegar-water mixture.

A Recipe for Air
Learners use M&Ms® (or any other multi-color, equally-sized small candy or pieces) to create a pie graph that expresses the composition of air.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.
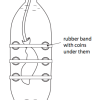
Submersibles and Marshmallows
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the difficulty of ocean exploration by human beings as they investigate water pressure.
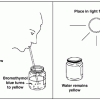
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Source Institutions
In this experiment using sprigs of Elodea, learners will observe a natural process that removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from Earth's atmosphere.
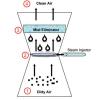
Washing Air
Learners observe and discuss a simple model of a wet scrubber, a device for cleaning industrial air pollution.

Hot Stuff!: Testing for Carbon Dioxide from Our Own Breath
Learners blow into balloons and collect their breath--carbon dioxide gas (CO2). They then blow the CO2 from the balloon into a solution of acid-base indicator.

A Merry-Go-Round for Dirty Air
Learners build a model of a pollution control device--a cyclone. A cyclone works by whirling the polluted air in a circle and accumulating particles on the edges of the container.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

Moving Without Wheels
In a class demonstration, learners observe a simple water cycle model to better understand its role in pollutant transport.

Hot Stuff!: Carbon Dioxide Extinguishes a Flame
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda creating carbon dioxide (CO2) in a bottle. The gas is poured out of a bottle onto a candle flame, putting out the candle.
