Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 37

Acid (and Base) Rainbows
Learners use red cabbage juice and pH indicator paper to test the acidity and basicity of household materials. The activity links this concept of acids and bases to acid rain and other pollutants.

How Can Gravity Make Something Go Up?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cheap, thin plastic garbage bags to quickly build a solar hot air balloon. In doing so, learners will explore why hot air rises.

Good News: We're on the Rise!
Learners build a simple aneroid barometer to learn about changes in barometric pressure and weather forecasting. They observe their barometer and record data over a period of days.

Acid Rain Effects
Learners conduct a simple experiment to model and explore the harmful effects of acid rain (vinegar) on living (green leaf and eggshell) and non-living (paper clip) objects.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.
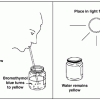
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Source Institutions
In this experiment using sprigs of Elodea, learners will observe a natural process that removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from Earth's atmosphere.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

What Color is Your Air Today?
Learners develop awareness and understanding of the daily air quality using the Air Quality Index (AQI) listed in the newspaper or online.

Leaf it to Me
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the effect of transpiration as water is moved from the ground to the atmosphere.
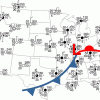
Drawing Conclusions
Source Institutions
In this weather forecasting activity, learners determine the location of cold and warm fronts on weather plot maps.
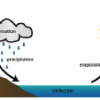
The Water Cycle
Source Institutions
Did you know that the water we use today is the same water found on Earth millions of years ago? The Earth constantly uses and recycles water in a process called the water cycle.
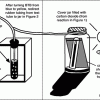
How Greenhouse Gases Absorb Heat
Source Institutions
Learners observe two model atmospheres -- one with normal atmospheric composition and another with an elevated concentration of carbon dioxide.

The Carbon Cycle Game
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take on the role of a carbon atom and record which reservoirs in the carbon cycle they visit.

Mapping Greenhouse Gas Emissions Where You Live
Source Institutions
In this lesson plan, learners examine some of the of greenhouse gas emissions sources in their community.

Weather Stations: Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test how cornstarch and glitter in water move when disturbed. Learners compare their observations with videos of Jupiter's and Earth's storm movements.

What-a-cycle
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners act as water molecules and travel through parts of the water cycle to discover that it is more complex than just water moving from the ground to the atmosphere.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Corals and Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate how increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the burning of fossil fuels is changing the acidity (pH) of the ocean and affecting coral reefs and other marin

What is a “Convection Cell”?
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners can observe a number of small convection cells generated from a mixture of aluminum powder and silicon oil on a hot plate.
