Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 32

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #4
Learners test two jars containing soil, one covered and one open, for changes in temperature. After placing the jars in the Sun, learners discover that the covered jar cools down more slowly.

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #1
Learners test two jars, one containing plain air and one containing carbon dioxide gas, to see their reactions to temperature changes.

Plugged in to CO2
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate various appliances and electronics, discovering how much energy each uses and how much carbon dioxide (CO2) is released to produce that energy.

What's In Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test to see if carbon dioxide is present in the air we breathe in and out by using a detector made from red cabbage.

Introduction to the Scientific Method
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 26 of the PDF), learners make observations, formulate hypotheses and design a controlled experiment, based on the reaction of carbon dioxide with calcium hydroxide.

Hot Stuff!: Testing for Carbon Dioxide from Our Own Breath
Learners blow into balloons and collect their breath--carbon dioxide gas (CO2). They then blow the CO2 from the balloon into a solution of acid-base indicator.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

Hot Stuff!: Carbon Dioxide Extinguishes a Flame
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda creating carbon dioxide (CO2) in a bottle. The gas is poured out of a bottle onto a candle flame, putting out the candle.

Earth Atmosphere Composition
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use rice grains to model the composition of the atmosphere of the Earth today and in 1880. Learners assemble the model while measuring percentages.
Let's Make Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use gumdrops and toothpicks to model the composition and molecular structure of three greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4).

Breathing Blue
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test exhaled breath for carbon dioxide and learn how to use an indicator as a simple way to measure pH.

Hot Stuff!: Creating and Testing for Carbon Dioxide
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda reacting to form carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.

Hot Stuff!: Testing Ice
In this demonstration, learners compare and contrast regular water ice to dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide). Both samples are placed in a solution of acid-base indicator.
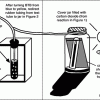
How Greenhouse Gases Absorb Heat
Source Institutions
Learners observe two model atmospheres -- one with normal atmospheric composition and another with an elevated concentration of carbon dioxide.

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #2
Learners test two jars containing hot water, one covered with plastic and one open, for changes in temperature.

The Carbon Cycle Game
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take on the role of a carbon atom and record which reservoirs in the carbon cycle they visit.

Mapping Greenhouse Gas Emissions Where You Live
Source Institutions
In this lesson plan, learners examine some of the of greenhouse gas emissions sources in their community.

Automotive Emissions and the Greenhouse Effect
Source Institutions
In this activity about global climate change, learners will conduct an experiment and collect data to compare the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in four different sources of gases.

Corals and Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate how increased carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the burning of fossil fuels is changing the acidity (pH) of the ocean and affecting coral reefs and other marin

Make a Terrarium
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a miniature greenhouse or "terrarium" to explore the greenhouse effect.
