Search Results
Showing results 1 to 13 of 13

Polyatomic Ion Bingo
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can play this game to learn about the major polyatomic ions (an ion that consists of two different elements).

What's in the Water?: Biotic and Abiotic Elements in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this investigation learners explore the differences between, and interdependence of, living and nonliving elements in a water ecosystem.
Properties of Metals
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the properties of metals at four stations. The stations include A) Magnetism and Breakfast Cereal; B) Conductivity of Metals; C) Alloys; and D) Metal Plating.
Periodic Pegboard
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use pegboard and straws to build a three-dimensional model of the periodic table.

Marine Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In the wild, small crustaceans known as brine shrimp live in marine habitats such as saltwater lakes.
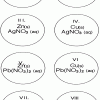
Single Replacement Micro-Reactions
Source Institutions
In this chemistry activity, learners use common chemicals and metals to explore single replacement reactions.

Watercolor
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use chemistry to create a night sky watercolor painting. They will experiment to learn the effects of mixing crayon, salt, and lemon juice with water color paints.

Freshwater Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a freshwater ecosystem in a large plastic bottle. Learners cut and prepare bottles, then fill with water, aquatic plants, snails and fish.

A Universe Without Supernovae
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity illustrates the value of supernovae in the universe.

Having a Gas with Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a simple electrolysis device. With this device, learners can decompose water into its elemental components: hydrogen and oxygen gas.

Nuclear Fusion
Source Institutions
This simple and engaging astronomy activity explains nuclear fusion and how radiation is generated by stars, using marshmallows as a model.

Production of a Gas: Controlling a Chemical Reaction
Source Institutions
Learners mix vinegar and baking soda to produce a gas. With the addition of a bit of liquid soap, the gas becomes trapped in measurable bubbles.

Change in Temperature: Exothermic Reaction
Source Institutions
Learners add calcium chloride to a baking soda solution and observe an increase in temperature along with the production of a gas and a white precipitate. These are all signs of a chemical reaction.
