Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 24

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.
Heavyweight Champion: Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners confront their perceptions of gravity in the solar system.

Landing the Rover
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 19-24 of PDF), learners "land" a model Lunar Rover in a model Landing Pod (both previously built in activities #3 and #4 in PDF).

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Fast Rusting
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out if steel wool will weigh more or less when it is burned. Learners will explore the effects of oxidation and rusting on the steel wool.

Space Stations: Beans in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform 20 arm curls with cans that simulate the weight of beans on Earth versus the weights of the same number of beans on the Moon and in space.
Weighty Questions
Source Institutions
In this activity about humans and space travel (page 1 of PDF), learners compare and contrast the behavior of a water-filled plastic bag, both outside and inside of a container of water.
Trash Talkin'
In this activity, learners collect, categorize, weigh and analyze classroom trash and discuss ways that engineers have helped to reduce solid waste.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
MarsBound!: Mission to the Red Planet
Source Institutions
MarsBound! is an engineering simulation activity in which learners use realistic techniques to plan a mission to Mars.
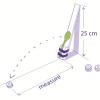
Volcanic Material Catapult Investigation
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Lava Flow Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into the relationship between an object’s mass and the distance it is thrown by a catapult.

Space Jell-O
Source Institutions
Albert Einstein proved that space bends around anything that has mass. This activity uses Jell-O's ability to bend around objects as a model for space bending around planets and stars.
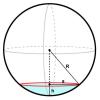
Mass, Area, Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 18 of PDF), learners will measure the volume of impact craters created by projectiles of different masses.

Does Air Weigh Anything?
Source Institutions
The demonstration/experiment provides quick proof that air has mass.

Sea Level: On The Rise
Source Institutions
Learners will understand the relationship between climate change and sea-level rise.

Weight in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are challenged to calculate their own weight on various planets using a scale and calculator. Older learners may be challenged to do so without using calculators.
Design a Lunar Rover!
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 2-10 of PDF), learners design and build a model of a Lunar Transport Rover that will carry equipment and people on the surface of the Moon.
