Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 25

Modeling Day and Night
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 1 of the PDF), learners make a "mini-globe" to investigate the causes of day and night on our planet.

Hot Equator, Cold Poles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use multiple thermometers, placed at different angles, and a lamp to investigate why some places on Earth's surface are much hotter than others.

Water Illusions: Refraction & Magnification
Source Institutions
Learners demonstrate how water can distort, refract and magnify light.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

Make a Prism
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make their own prism and use a glass of water to separate sunlight into different colors.

Zero-Energy Housing
In this activity, learners investigate passive solar building design with a focus solely on heating.
Light on Other Planets
Source Institutions
In this math-based activity, learners model the intensity of light at various distances from a light source, and understand how astronomers measure the amount of sunlight that hits our planet and othe

Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 11 of PDF), learners compare the air pressure within a dark and a light bottle both heated by the sun, and discover that solar energy can be collected and stored in many ways

Solar Water Heater
Learners work in teams to design and build solar water heating devices that mimic those used in residences to capture energy in the form of solar radiation and convert it to thermal energy.

Crystal Creations: Grow Spikes of Crystals in the Sun
Source Institutions
This activity shows you how to make amazing crystal spikes using Epsom salt and the sun.
Rainbow in the Room
Source Institutions
This activity generates learner excitement about light through the creation of a room-sized rainbow.

The Shadow Knows II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of a shadow and use the distance from the equator to calculate the circumference of the earth.

Toasty Wind
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners use a toaster to investigate the source for the Earth's wind. Learners hold a pinwheel above a toaster to discover that rising heat causes wind.

Water Cycle in a Bag
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a biosphere in a baggie.

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.

Make a UV Detector
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use tonic water to detect ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun and explore the concept of fluorescence.

Ancient Sun Observations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own Sun tracker to explore how ancient civilizations around the world studied the Sun.

Cooking With the Sun
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple solar oven out of household materials to melt chocolate and marshmallow between graham crackers--known as s'mores.
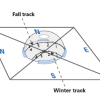
Reason for the Seasons
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 6 of the PDF), learners plot the path of the sun's apparent movement across the sky on two days, with the second day occurring two or three months after the first.

Mini Glacier Meltdown
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Glaciers Activity) is a full inquiry investigation about the different causes of glacial melt.
