Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 51

Electrical Fleas
Source Institutions
In this activity about electricity, learners explore how static electricity can make electric "fleas" jump up and down. Learners use a piece of wool cloth or fur to charge a sheet of acrylic plastic.

Fan Cart
Source Institutions
If a sailboat is stranded because there is no wind, is it possible to set up a fan on deck and blow wind into the sail to make the boat move?
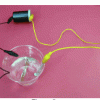
Electroplating
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, learners will explore two examples of electroplating.
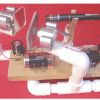
Laser Lissajous: PVC Version
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a laser pointer and two small rotating mirrors to create a variety of fascinating patterns, which can be easily and dramatically projected on a wall or screen.

Make a Sun Clock: Tell Time with the Sun
Source Institutions
Before there were clocks, people used shadows to tell time. In this outdoor activity, learners will discover how to tell time using only a compass, a pencil, a handy printout, and a sunny day.

Eddy Currents
Source Institutions
In this activity related to magnetism and electricity, learners discover that a magnet falls more slowly through a metallic tube than it does through a nonmetallic tube.

Stripped-down Motor
Source Institutions
In this activity, you'll make an electric motor--a simple version of the electric motors found in toys, tools, and appliances everywhere.
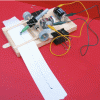
Paper Tape Motion Timer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a recording timer made from simple materials (e.g., small dc motor, sharpie pen, craft sticks, adding machine paper tape, etc.).

Fast Rusting
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out if steel wool will weigh more or less when it is burned. Learners will explore the effects of oxidation and rusting on the steel wool.

Circles of Magnetism I
Source Institutions
In this activity related to magnetism and electricity, learners create a magnetic field that's stronger than the Earth's magnetic field.

Tape Electroscope
Source Institutions
In this simple activity, learners create an electroscope by sticking two short pieces of magic tape together and then pulling them apart to find the sign of the charge on an unknown charged object.
Floating Paperclip and Other Surface Tension Experiments
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment with surface tension using everyday household items such as strawberry baskets, paperclips, liquid dish soap, and pepper.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.
Stretch the Chain and See the Light
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use their strength to light a light bulb. A chain made from paper clips is placed in series with a battery and flashlight bulb.

Kosher Dill Current: Make Your Own Battery!
Source Institutions
This is an activity that demonstrates how batteries work using simple household materials. Learners use a pickle, aluminum foil and a pencil to create an electrical circuit that powers a buzzer.
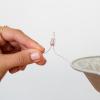
Charge and Carry
Source Institutions
In this activity about electricity, learners produce a spark that they can feel, see, and hear. Learners rub a Styrofoam plate with wool to give it an electric charge.

Electrostatic Water Attraction
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a simple experiment to see how electrically charged things like plastic attract electrically neutral things like water.
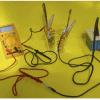
Cake by Conduction
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, cook a cake using the heat produced when the cake batter conducts an electric current.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
Electrolysis is the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen. This Exploratorium activity allows learners to visualize the process with an acid-based indicator.
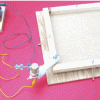
Shake Table
Source Institutions
This activity guide includes instructions on how to build a "Shake Table" by mounting an eccentric mass (off center) on the shaft of a small dc motor.
