Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 22

Growing Food From Scraps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore vegetative propagation while preparing food scraps to grow into plants.

Iodine Investigators!
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 7 of the PDF (Chemistry—It’s Elemental), learners use iodine to identify foods that contain starch.

Fuel for Living Things
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe what happens when yeast cells are provided with a source of food (sugar). Red cabbage "juice" will serve as an indicator for the presence of carbon dioxide.
Candy Chemosynthesis
Source Institutions
In this activity, groups of learners work together to create edible models of chemicals involved in autotrophic nutrition.
Do Plants Need Light?
Source Institutions
In this food science activity, learners conduct an experiment that demonstrates the importance of light to plants.

Bury Me Not!
Source Institutions
This activity (page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs) is a full inquiry investigation into decomposition.

Color-Changing Carnations
Source Institutions
Learners place cut flowers in colored water and observe how the flowers change. The flowers absorb the water through the stem and leaves.

How Plants Grow
Source Institutions
In this biology activity (page 3 of the PDF), learners will explore how plants turn sunlight into food through a process called photosynthesis.
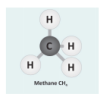
Let's Make Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use gumdrops and toothpicks to model the composition and molecular structure of three greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4).

Capturing Carbon Dioxide
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate carbon sequestration by creating a carbonated beverage out of apple juice and dry ice.

Diet Light
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how the added sugar in a can of soda affects its density and thus, its ability to float in water.

Amphibian Skin
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the concept of permeability to better understand why amphibians are extremely sensitive to pollution.

Salt 'n Lighter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that as the salinity of water increases, the density increases as well. Learners prove this by attempting to float fresh eggs in saltwater and freshwater.
Spill Spread
Source Institutions
In this simulation, learners explore how ocean currents spread all kinds of pollution—including oil spills, sewage, pesticides and factory waste—far beyond where the pollution originates.

Natural Indicators
Source Institutions
Learners combine different plant solutions -- made from fruits, vegetables, and flowers -- with equal amounts of vinegar (acid), water (neutral), and ammonia (base).

Save Your Skin
Source Institutions
This is a fun activity about the power of the Sun and the importance of using sunscreen to protect your sensitive skin from its rays.

A Funny Taste
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the different salinities of various sources of water by taste-testing.

Avogadro's Bubbly Adventure
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 7 of the PDF, learners investigate the solubility of gas in water at different temperatures. This experiment will help learners determine if temperature affects solubility.
Leaves: Extracting Pigments
Source Institutions
In this fun, hands-on autumn activity, learners experiment to discover whether the colored substances in leaves can be separated from the leaves.

We all Scream for Ice Cream
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe how salinity affects the freezing point of water by making and enjoying ice cream.
