Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 29

Effect of Environment on Plant Growth
Source Institutions
The purpose of this plant biotechnology activity is to demonstrate the effect of changes in the environment on the growth and fertility of landscape grasses and crop grasses such as wheat and rice.

Do Plants Need Sunlight?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners find out what happens when they cover leaves with pieces of black construction paper. This activity shows learners that plants need sunlight to survive.

How Plants Grow
Source Institutions
In this biology activity (page 3 of the PDF), learners will explore how plants turn sunlight into food through a process called photosynthesis.
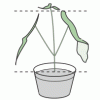
Do Plants Need Light?
Source Institutions
In this food science activity, learners conduct an experiment that demonstrates the importance of light to plants.

Photosynthesis and Transpiration
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 7 of the PDF (Plants—The Green Machines), learners examine the effects that light and air have on green plants.

Natural Indicators
Source Institutions
Learners combine different plant solutions -- made from fruits, vegetables, and flowers -- with equal amounts of vinegar (acid), water (neutral), and ammonia (base).

How Might Elevated CO2 Affect Plants
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to investigate the effect of elevated levels on CO2 on plant growth.

Growing Food From Scraps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore vegetative propagation while preparing food scraps to grow into plants.

Moving On Up: Capillary Action 1
Source Institutions
Over the course of several days, learners explore the property of water that helps plants move water from roots to leaves or gives paper towels the capacity to soak up water.

Paper Chromatography with Leaves
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 5 of the PDF (Plants—The Green Machines), learners use chromatography to separate and identify pigments within various leaves.

Sand, Plants and Pants
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how the application of nano-sized particles or coatings can change a bigger material’s properties.

Super Soil
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners make their own organic-rich soil. Depending on where this activity is done, learners will probably discover that their local soil is low in organic matter.

Moisture Makers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners compare the moisture released from different kinds of leaves and from different parts of the same leaf, by observing the color change of cobalt chloride paper.

Seeds: Roots and Shoots
Source Institutions
In this indepth hands-on activity, learners build a structure that allows them to observe the growth of roots and the correlation between root growth and stem extension.

Composting
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity, learners research what is essential for plant life and the necessary components of soil to support plants.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 2
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 7), learners explore the meaning of a "carbon sink." Using simple props, learners and/or an educator demonstrate how plants act as carbon sinks and how greenhouse gases cause
Mercury in the Environment
Source Institutions
In this environmental science lesson, learners will examine the dangers of mercury and how humans contribute to growing mercury emissions on Earth.

Color-Changing Carnations
Source Institutions
Learners place cut flowers in colored water and observe how the flowers change. The flowers absorb the water through the stem and leaves.

The Carbon Cycle and its Role in Climate Change: Activity 3
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the human influences on the carbon cycle and examine how fossil fuels release carbon.

Water "Digs" It!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate soil erosion. Learners set up a simulation to observe how water can change the land and move nutrients from one place to another.
