Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 33

Spring Scale Engineering
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how spring scales work and how they are used for non-exact weight measurement.

Gieant Sieve Sorter
Source Institutions
This Exploratorium activity explores size and scale. Through four levels of screen sizes, learners can sort out objects of different sizes.

Does Size Make a Difference?
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 15 of the PDF, discover how materials and physical forces behave differently at the nanoscale.

What is a Nanometer?
Source Institutions
This lesson focuses on how to measure at the nanoscale and provides learners with an understanding how small a nanometer really is.
Forwards and Backwards: pH and Indicators
Source Institutions
Visitors prepare six solutions combining vinegar and ammonia that range incrementally from acid (all vinegar) to base (all ammonia).
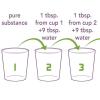
Sniffing for a Billionth
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 4 of the PDF under What's Nano? Activity) about size and scale.

Sliding and Stuttering
Source Institutions
Learners use a spring scale to drag an object such as a ceramic coffee cup along a table top or the floor.

Exploring at the Nanoscale
Source Institutions
This lesson focuses on how nanotechnology has impacted our society and how engineers have learned to explore the world at the nanoscale.

Leaning Tower of Pasta
Learners build structures from spaghetti and marshmallows to determine which structures are able to handle the greatest load.

Blow-and-Go Parachute
Learners make a skydiver and parachute contraption and launch it. They see that the drag created by air resistance slows the descent of skydivers as they travel back to Earth.

Be a Scanning Probe Microscope
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate Scanning Probe Microscopes (SPM) and then work in teams using a pencil to explore and identify the shape of objects they cannot see, just as SPMs do at the nano

A Merry-Go-Round for Dirty Air
Learners build a model of a pollution control device--a cyclone. A cyclone works by whirling the polluted air in a circle and accumulating particles on the edges of the container.

Straining Out the Dirt
Learners take on the role of environmental engineers as they design water filters.

Dripping Wet or Dry as a Bone?
Learners investigate the concept of humidity by using a dry and wet sponge as a model. They determine a model for 100% humidity, a sponge saturated with water.

Good News: We're on the Rise!
Learners build a simple aneroid barometer to learn about changes in barometric pressure and weather forecasting. They observe their barometer and record data over a period of days.

Hot Stuff!: Testing for Carbon Dioxide from Our Own Breath
Learners blow into balloons and collect their breath--carbon dioxide gas (CO2). They then blow the CO2 from the balloon into a solution of acid-base indicator.

Try Your Hand at Nano
Source Institutions
This lesson focuses on two simple activities that younger learners can do to gain an appreciation of nanotechnology. First, learners measure their hands in nanometers.

Hot Stuff!: Investigation #4
Learners test two jars containing soil, one covered and one open, for changes in temperature. After placing the jars in the Sun, learners discover that the covered jar cools down more slowly.

Acid (and Base) Rainbows
Learners use red cabbage juice and pH indicator paper to test the acidity and basicity of household materials. The activity links this concept of acids and bases to acid rain and other pollutants.

