Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 21

Heat Capacity: Can't Take the Heat?
Source Institutions
Why is ocean water sometimes the warmest when the average daily air temperature starts to drop? In this activity, learners explore the differing heat capacities of water and air using real data.

PVC Water Squirter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a water squirter using a PVC pipe, dowel, and foam. This activity is great for the summer time and introduces learners to forces and water pressure.
Under Pressure
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners examine how pressure affects water flow. In small groups, learners work with water and a soda bottle, and then relate their findings to pressure in the deep ocean.

Inverted Bottles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate convection by using food coloring and water of different temperatures.

Rates of Change: Bottles and Divers
Source Institutions
In this math lesson (page 2 of the PDF), learners use bottles of various shapes to explore the abstract concept of rate of change.
Investigating Density Currents
Source Institutions
In this lab activity, learners explore how to initiate a density current. Learners measure six flasks with different concentrations of salt and water (colored blue).
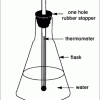
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Inflate-a-mole
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find the volume of one mole of gas. Learners capture sublimated gas from dry ice in a ziploc bag and use water displacement to measure its volume.

Thermal Energy Put to Work
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners determine whether thermal energy can be used for work.
Build A Hydrometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore how a hydrometer works by building a working model and conducting experiments.
Investigating Convection
Source Institutions
This experiment is designed to illustrate how fluids, including water, have the ability to flow.

How Big is Small
Source Institutions
In this classic hands-on activity, learners estimate the length of a molecule by floating a fatty acid (oleic acid) on water.

A Hurricane's Storm Surge Affects our Estuaries
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a coastal landmass from sand and add features such as tidal creeks and barrier islands.

A Cubic Foot Per Second
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure and calculate the amount of cubic feet various containers contain. Next, learners investigate cubic feet per second (cps), by carrying jugs in one second.

Instant Ice Cream with a Dry Ice Bath
Source Institutions
In this chemistry meets cooking activity, learners make carbonated, vanilla ice cream using dry ice and denatured ethanol, which are both inexpensive and accessible.

Mass of the Earth
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use basic measurements of the Earth and pieces of rock and iron to estimate the mass of the Earth.

Plot the Dot: A Graphical Approach to Density
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to determine the mass and volume of four samples: glass marbles, steel washers or nuts, pieces of pine wood, and pieces of PVC pipe.

Linear Functions: Mystery Liquids
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners analyze the density of liquids in order to explore linear functions.

Counting With Quadrants
Source Institutions
Millions of organisms can live in and around a body of water.
