Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 23

Color-Changing Carnations
Source Institutions
Learners place cut flowers in colored water and observe how the flowers change. The flowers absorb the water through the stem and leaves.

Moisture Makers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners compare the moisture released from different kinds of leaves and from different parts of the same leaf, by observing the color change of cobalt chloride paper.
Water Molds (Oomycetes)
Source Institutions
In this laboratory activity, learners use a simple procedure to bait oomycetes from water and/ or soil and then examine these fungus-like organisms with the microscope to see how they look.

Nutrients in an Estuary
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model estuaries, artificially enriching both fresh and salt water samples with different amounts of nutrients and observing the growth of algae over several weeks.

Human Impact on Estuaries: A Terrible Spill in Grand Bay
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a model of a pollution spill that occurred at Bangs Lake in Mississippi and measure water quality parameters in their model.
Close, Closer, Closest
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment that models a chromatography-like process called electrophoresis, a process used to analyze DNA.
DNA Extraction: Look at your genes!
Source Institutions
Extract your DNA from your very own cells! First, learners swish salt water in their mouth to collect cheek cells and spit the water into a glass.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Single-Cell Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a soil and water model of a single-cell life environment and study living microorganisms.

Diffusion & Osmosis with Data Analysis
Source Institutions
This three-part lab helps learners understand the essential principles governing diffusion and osmosis.
The Dead Zone: A Marine Horror Story
Source Institutions
In this environmental science and data analysis activity, learners work in groups to track a Dead Zone (decreased dissolved oxygen content of a body of water) using water quality data from the Nutrien

Chemical Breath
Source Institutions
This is a chemistry lab activity about solutions (page 7 of the PDF). Learners see firsthand how chemicals in a solution can combine to form an entirely different substance.

Make a "Mummy"
Source Institutions
The Ancient Egyptians used a naturally-occurring salt from the banks of the Nile River, called natron, to mummify their dead.

Small Habitats
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a model of a self-sustaining habitat (growing grass and beans from seeds).

Growing Food From Scraps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore vegetative propagation while preparing food scraps to grow into plants.
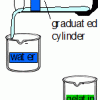
Natural Buffers
Source Institutions
Learners use a universal indicator to test the amount of sodium hydroxide needed to change the pH of plain water compared with the amount needed to change the pH of gelatin.

Make a Heart Valve
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a model of a one-way heart valve to investigate how a heart controls the direction of blood flow.

Natural Indicators
Source Institutions
Learners combine different plant solutions -- made from fruits, vegetables, and flowers -- with equal amounts of vinegar (acid), water (neutral), and ammonia (base).
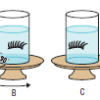
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the

Moldy Jell-O
Source Institutions
In this laboratory activity, learners design an experiment to evaluate how environmental factors influence the growth of molds.
