Search Results
Showing results 1 to 16 of 16
Rain Machine (Solar Still)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to build simple solar stills filled with salt water. After the stills are complete, learners observe what happens when they place the stills in the sun.

Balloon Impacts
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure the diameter of their water balloons, model an impact, measure the diameter of the “crater” area, and determine the ratio of impactor to crater.

Portable Potable Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use plastic water bottles, wood, and water to build an inexpensive and portable tool to demonstrate one atmosphere of pressure at sea level.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Kid Moon: Splat!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model ancient lunar impacts using water balloons.

Canned Heat
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how light and dark colored objects absorb the Sun's radiations at different rates.
Making An Impact!
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 14 of PDF), learners use a pan full of flour and some rocks to create a moonscape.
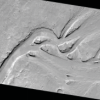
Mars from Above: Carving Channels
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create channel features with flowing water, comparing their observations to real images of Mars and Earth taken by satellites/orbiters.

Geyser
Source Institutions
This Exploratorium activity can be used in many contexts because geysers are great opportunities for learning about heat and temperature changes as well as geological/space science phenomena.

Solar Cooker
Source Institutions
Learners build a simple solar oven from a shoebox, black construction paper, and aluminum foil. Over the course of a few hours, the oven heats up water enough to brew tea.

Habitable Worlds
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners consider environmental conditions—temperature, presence of water, atmosphere, sunlight, and chemical composition—on planets and moons in our solar system to determine

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Exploring Ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners explore UV rays from the Sun and ways to protect against these potentially harmful rays.

Cook Up a Comet
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 5 of PDF), learners use dry ice and household materials to make scientifically accurate models of comets.

Teen Moon: Moon Ooze
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model how the Moon's volcanic period reshaped its earlier features.
