Search Results
Showing results 1 to 13 of 13
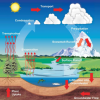
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

Balloon Impacts
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure the diameter of their water balloons, model an impact, measure the diameter of the “crater” area, and determine the ratio of impactor to crater.

Exploring the Universe: Ice Orbs
Source Institutions
“Exploring the Solar System: Ice Orbs” is a hands-on activity in which visitors investigate a frozen orb, trying to learn about objects hidden inside.

Portable Potable Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use plastic water bottles, wood, and water to build an inexpensive and portable tool to demonstrate one atmosphere of pressure at sea level.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).
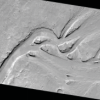
Mars from Above: Carving Channels
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create channel features with flowing water, comparing their observations to real images of Mars and Earth taken by satellites/orbiters.

Geyser
Source Institutions
This Exploratorium activity can be used in many contexts because geysers are great opportunities for learning about heat and temperature changes as well as geological/space science phenomena.

Signs of Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners examine photo images of Earth taken from space, and attempt to identify and explain some of our planet's geological features.

Weather Stations: Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test how cornstarch and glitter in water move when disturbed. Learners compare their observations with videos of Jupiter's and Earth's storm movements.

Habitable Worlds
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners consider environmental conditions—temperature, presence of water, atmosphere, sunlight, and chemical composition—on planets and moons in our solar system to determine

Ice on Mars
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use sand and ice cubes to create a model of permafrost and the effects of the ice melting through the surface.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

It's a Gas, Man
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover if carbon dioxide has an effect on temperature.
