Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 24
Weathering and Erosion
Source Institutions
In this multi-station lab, learners conduct a series of experiments to explore the processes and effects of weathering and erosion.

How Boulders Are Born
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners review and discuss weathering, erosion and mass wasting, to gain a stronger understanding of how Hickory Run’s Boulder Field was formed after the Laurentide Continental Glac

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.

Do Cities Affect the Weather?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore clouds and how they form.

Measure the Pressure: The "Wet" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.

Measure the Pressure II: The "Dry" Barometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use simple items to construct a device for indicating air pressure changes.
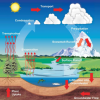
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

How Much Water is in that Cloud?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners working in pairs saturate a cotton ball using water drops from an eyedropper to demonstrate the high water capacity of clouds.

What is a “Convection Cell”?
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners can observe a number of small convection cells generated from a mixture of aluminum powder and silicon oil on a hot plate.

Good News: We're on the Rise!
Learners build a simple aneroid barometer to learn about changes in barometric pressure and weather forecasting. They observe their barometer and record data over a period of days.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

A Degrading Experience
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 27, learners perform an experiment to learn about how different types of marine debris degrade and how weather and sunlight affect the rate of degradation.

Where Does the Wind Blow?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate wind by comparing the force of wind in different locations. Learners build wind-o-meters out of wooden sticks and strips of paper.

Regolith Formation
Source Institutions
In this three-part activity, learners use food to determine the effects of wind, sandblasting and water on regolith (dust) formation and deposition on Earth.
Making Regolith
Source Institutions
This lesson will helps learners answer the question: How does the bombardment of micrometeoroids make regolith on the moon?
How is Coastal Temperature Influenced by the Great Lakes and the Ocean?
Source Institutions
In this two-part lesson, learners discover how large bodies of water can serve as a heat source or sink at different times and how proximity to water moderates climate along the coast.

Sunblock Investigation
Source Institutions
In this "Sid the Science Kid" activity, learners set up a simple experiment to find out how sunscreen counteracts the effects of the sun.

Making Sense of Sensors
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore sensors and focus specifically on how to measure humidity using a sensor.

Measuring the Wind
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how anemometers work to record wind speeds and how the equipment has undergone engineering adaptations over time.

We all Scream for Ice Cream
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe how salinity affects the freezing point of water by making and enjoying ice cream.
