Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 31
The Daily Ups and Downs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners graph 48 hourly air temperatures from a local weather observation site and observe the diurnal temperature variations.

Make Your Own Weather Station
Source Institutions
This three-part activity shows learners how to build three meteorology tools: a wind vane, a rain gauge, and a barometer.
Weather Forecasting
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Forecasting) is a full inquiry investigation into meteorology and forecasting.

Gravestone Weathering
Source Institutions
In this activity (located on pages 9-14 of PDF), learners visit a cemetery to examine the distinguishing characteristics of rock weathering.

Weather Stations: Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test how cornstarch and glitter in water move when disturbed. Learners compare their observations with videos of Jupiter's and Earth's storm movements.

Do Cities Affect the Weather?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore clouds and how they form.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Space Weather Action Center
Source Institutions
In this interdisciplinary activity, learners create a Space Weather Action Center (SWAC) to monitor solar storms and develop real SWAC news reports.
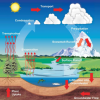
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

How Much Water is in that Cloud?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners working in pairs saturate a cotton ball using water drops from an eyedropper to demonstrate the high water capacity of clouds.

What is a “Convection Cell”?
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners can observe a number of small convection cells generated from a mixture of aluminum powder and silicon oil on a hot plate.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

A Degrading Experience
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 27, learners perform an experiment to learn about how different types of marine debris degrade and how weather and sunlight affect the rate of degradation.

Cloud Fun
Source Institutions
Learners complete a series of hands-on and investigative activities to explore cumulus clouds.

Creating a Soil Map
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate soil conditions by creating a soil map. Learners record soil characteristics and compare the conditions of soil in different grid sections.

Regolith Formation
Source Institutions
In this three-part activity, learners use food to determine the effects of wind, sandblasting and water on regolith (dust) formation and deposition on Earth.
Making Regolith
Source Institutions
This lesson will helps learners answer the question: How does the bombardment of micrometeoroids make regolith on the moon?

Diet Light
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how the added sugar in a can of soda affects its density and thus, its ability to float in water.

Erosion
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model erosion using a clear shoebox and sand or soil.
How is Coastal Temperature Influenced by the Great Lakes and the Ocean?
Source Institutions
In this two-part lesson, learners discover how large bodies of water can serve as a heat source or sink at different times and how proximity to water moderates climate along the coast.
