Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 46

Balancing Act
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 6 of the PDF), learners will build a class 1 lever and hypothesize and test the distances two objects need to be placed from the fulcrum in order to balance.
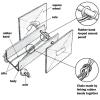
Roving on the Moon
Add to list DetailsIn this design challenge activity, learners build a rubber band-powered rover that can scramble across the room.
Periodic Pegboard
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use pegboard and straws to build a three-dimensional model of the periodic table.

Combustion
Source Institutions
In this chemistry activity, learners discover that the weight of the product of combustion is greater than that of the starting material.
MarsBound!: Mission to the Red Planet
Source Institutions
MarsBound! is an engineering simulation activity in which learners use realistic techniques to plan a mission to Mars.
Dollar Bill Grab
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners observe as two cola bottles and a dollar bill are arranged in a specific order: one bottle, upside down and filled with water, is placed on top of another bottle, with

Space Jell-O
Source Institutions
Albert Einstein proved that space bends around anything that has mass. This activity uses Jell-O's ability to bend around objects as a model for space bending around planets and stars.

Rubber Band newton Scale
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a simple spring-like scale using a rubber band instead of a spring, and calibrate the scale in newtons (N).

Inverted Bottles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate convection by using food coloring and water of different temperatures.

Float Your Boat
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners will explore buoyancy.

Weight in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are challenged to calculate their own weight on various planets using a scale and calculator. Older learners may be challenged to do so without using calculators.

Spring Scale Engineering
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how spring scales work and how they are used for non-exact weight measurement.
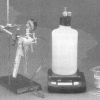
As Light as Air
Source Institutions
Learners measure a bottle full of air, and then use a vacuum pump to remove the air. When they re-weigh the bottle, learners find the mass is about 0.8g less.

Statue Display Tower
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners design, build, test and redesign a display tower that will meet a specific set of criteria and constraints.

Get the Porridge Just Right
Source Institutions
Learners set up three different bowls, each with a different mass of oatmeal. Learners monitor the temperature of the oatmeal and find that larger masses take longer to cool.

Balanced Budget Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners balance chemical equations and discover the law of conservation of mass. Learners use coins to model molecules to balance the equations.

Scaling an Atom
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a scale model of an atom to see how big or how small an atom is compared to its nucleus. Learners will realize that most of matter is just empty space!

Newton's 2nd Law: Inquiry Approach
Source Institutions
In this lab activity, learners act as fellow scientists and colleagues of Isaac Newton. He has asked them to independently test his ideas on the nature of motion, in particular his 2nd Law.

Falling Feather
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners recreate Galileo's famous experiment, in which he dropped a heavy weight and a light weight from the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa to show that both weights fall
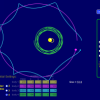
My Solar System
Source Institutions
In this online activity, learners build their own system of heavenly bodies and watch the gravitational ballet.
