Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 68

Gravity and Falling
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners experiment with a bucket, stretchy fabric, marbles, and weights to discover some basics about gravity.

Fly a Hot-Air Balloon
Source Institutions
Learners assemble a hot-air balloon from tissue paper. The heated air (from a heat gun) inside the balloon is less dense than the surrounding air and causes the balloon to float.

Volume, Mass, and Density Boxes
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can utilize it to investigate volume, mass, and density.

Balancing Stick
Source Institutions
In this quick and simple activity, learners explore how the distribution of the mass of an object determines the position of its center of gravity, its angular momentum, and your ability to balance it

Conservation of Mass
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can participate to learn about conservation of gas. This is one of the classic experiments using baking soda and vinegar.
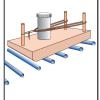
Newton Car
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in teams to investigate the relationship between mass, acceleration, and force as described in Newton's second law of motion.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Uplifting Force: Buoyancy & Density
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners explore the force known as buoyancy by placing various objects into water and observing how they behave (for example, which sink more quickly, which float, how much wat

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
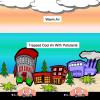
Turning the Air Upside Down: Convection Current Model
Learners see convection currents in action in this highly visual demonstration. Sealed bags of colored hot or cold water are immersed in tanks of water.
MarsBound!: Mission to the Red Planet
Source Institutions
MarsBound! is an engineering simulation activity in which learners use realistic techniques to plan a mission to Mars.

Downhill Race
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how two cylinders that look the same may roll down a ramp at different rates.

Changing the Density of an Object: Adding Material
Source Institutions
Learners see that a can of regular cola sinks while a can of diet cola floats. As a demonstration, bubble wrap is taped to the can of regular cola to make it float.
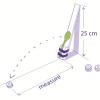
Volcanic Material Catapult Investigation
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Lava Flow Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into the relationship between an object’s mass and the distance it is thrown by a catapult.

Turning the Air Upside Down: Warm Air is Less Dense than Cool Air
Learners cover a bottle with a balloon. When they immerse the bottle in warm water, the balloon inflates. When they immerse the bottle in a bowl of ice, the balloon deflates.
Dollar Bill Grab
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners observe as two cola bottles and a dollar bill are arranged in a specific order: one bottle, upside down and filled with water, is placed on top of another bottle, with

Space Jell-O
Source Institutions
Albert Einstein proved that space bends around anything that has mass. This activity uses Jell-O's ability to bend around objects as a model for space bending around planets and stars.

Sink It
Source Institutions
Learners classify a variety of objects by their characteristics. They then design an experiment to determine which objects float or sink in water and add this characteristic to their classification.
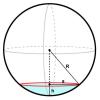
Mass, Area, Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 18 of PDF), learners will measure the volume of impact craters created by projectiles of different masses.
