Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 34

How Can Gravity Make Something Go Up?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cheap, thin plastic garbage bags to quickly build a solar hot air balloon. In doing so, learners will explore why hot air rises.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.
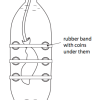
Submersibles and Marshmallows
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the difficulty of ocean exploration by human beings as they investigate water pressure.
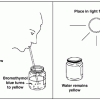
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Source Institutions
In this experiment using sprigs of Elodea, learners will observe a natural process that removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from Earth's atmosphere.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another

Earth Atmosphere Composition
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use rice grains to model the composition of the atmosphere of the Earth today and in 1880. Learners assemble the model while measuring percentages.
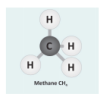
Let's Make Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use gumdrops and toothpicks to model the composition and molecular structure of three greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4).

Lifting Lemon
Source Institutions
In this physics demonstration, learners will be surprised when a lemon slice appears to magically levitate within a pint glass.

The Carbon Cycle Game
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take on the role of a carbon atom and record which reservoirs in the carbon cycle they visit.

Mapping Greenhouse Gas Emissions Where You Live
Source Institutions
In this lesson plan, learners examine some of the of greenhouse gas emissions sources in their community.

What-a-cycle
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners act as water molecules and travel through parts of the water cycle to discover that it is more complex than just water moving from the ground to the atmosphere.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Battling for Oxygen
Working in groups, learners model the continuous destruction and creation of ozone (O3) molecules, which occur in the ozone layer.

What is a “Convection Cell”?
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners can observe a number of small convection cells generated from a mixture of aluminum powder and silicon oil on a hot plate.
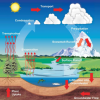
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.
Turning the Air Upside Down: Convection Current Model
Learners see convection currents in action in this highly visual demonstration. Sealed bags of colored hot or cold water are immersed in tanks of water.

I Can't Take the Pressure!
Learners develop an understanding of air pressure in two different activities.

Turning the Air Upside Down: Warm Air is Less Dense than Cool Air
Learners cover a bottle with a balloon. When they immerse the bottle in warm water, the balloon inflates. When they immerse the bottle in a bowl of ice, the balloon deflates.

Capturing Carbon Dioxide
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate carbon sequestration by creating a carbonated beverage out of apple juice and dry ice.
