Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 29

Crossing the Synaptic Gap
Source Institutions
In this neuroscience activity, learners conduct a simulation to demonstrate how multiple incoming signals influence the action of neurons.

DNA Extraction
Source Institutions
In this activity related to plant biotechnology, learners extract DNA from fruit to investigate how it looks and feels.

Let's Clone a Mouse, Mouse, Mouse...
Source Institutions
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) is a cloning method that involves transferring a nucleus from a somatic cell of the individual to be cloned to an enucleated egg.

Animal & Plant Cell Slides
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make slides of onion cells and their own cheek cells. Use this lab to teach learners how to prepare microscope slides and use a microscope.
Modeling Limits to Cell Size
Source Institutions
This investigation provides learners with a hands-on activity that simulates the changing relationship of surface areas-to-volume for a growing cell.

Why Circulate?
Source Institutions
In this activity related to the human circulatory system (on page 10 of the PDF), learners observe the dispersion of a drop of food coloring in water, draw conclusions about the movement of dissolved
Pathways with Friends
Source Institutions
Directed by instructional cards, learners kinesthetically model cell communication by acting as components in a cell signaling pathway.
Modeling an HIV Particle
Source Institutions
This activity helps learners visualize the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) by constructing three-dimensional HIV particle models from paper.
Magnifying and Observing Cells
Source Institutions
In this activity related to microbes, learners make slides of cells from an onion skin and Elodea (American or Canadian waterweed) to observe under a microscope.

What Cells Can I See in Muscle and Spinal Cord Tissues?
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 37 of the PDF), learners observe, on a prepared slide, muscle and spinal cord cells from a rat.
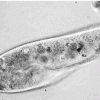
Observing Different Microbes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a microscope to examine three different microbes: bacteria, yeast and paramecia. Educator will need to prepare the yeast solution one day before the activity.

Coffee to Carbon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners place cards featuring biological structures in order by their relative size from largest to smallest.

Dealing Signals
Source Institutions
In this activity, use standard playing cards to introduce learners to cellular interactions such as cell to cell recognition and signal and receptor specificity.
Microarrays and Stem Cells
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use microarray technology to determine which genes are turned on and off at various points in the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells on their way to becoming pancreat

The Ladder of Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners identify the DNA base bars guanine, cytosine, thymine and adenine. Learners create a DNA model using colored paper clips to resemble these base pairs.

Using Bubbles to Explore Membranes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use bubbles to investigate the structure and unique properties of cell membranes. Bubbles serve as macroscopic models that mimic the cells' phospholipid bilayers.
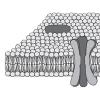
Build-A-Membrane
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners cut, fold, and paste paper representing biomolecules to create a three-dimensional cell membrane with embedded proteins.
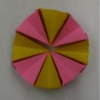
Paper Proteins
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use an origami template to design eight amino acids. Learners configure the amino acids to form a protein. Use this activity to introduce proteins and amino acids.

Is It Alive?
Source Institutions
What does it mean to be alive? Is a cactus alive? Is a seed alive? Is the air we breathe alive? What are the necessary characteristics?

Diffusion & Osmosis with Data Analysis
Source Institutions
This three-part lab helps learners understand the essential principles governing diffusion and osmosis.
