Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 41

Salt 'n Lighter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that as the salinity of water increases, the density increases as well. Learners prove this by attempting to float fresh eggs in saltwater and freshwater.

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.

Diet Light
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how the added sugar in a can of soda affects its density and thus, its ability to float in water.
Heavyweight Champion: Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners confront their perceptions of gravity in the solar system.

How Can Gravity Make Something Go Up?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cheap, thin plastic garbage bags to quickly build a solar hot air balloon. In doing so, learners will explore why hot air rises.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Oil Spill Cleanup
This hands-on experiment will provide learners with an understanding of the issues that surround environmental cleanup.

Submarine: Lift Bag Lander
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 4), learners create a submarine using a plastic sandwich bag. This is a fun way to learn about buoyancy and how captured gas can cause objects to float.

Infant Moon: Moon Mix!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the Moon's infancy and model how an ocean of molten rock (magma) helped shape the Moon that we see today.
Weighty Questions
Source Institutions
In this activity about humans and space travel (page 1 of PDF), learners compare and contrast the behavior of a water-filled plastic bag, both outside and inside of a container of water.

The Great Plankton Race
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are challenged to design a planktonic organism that will neither float like a cork nor sink like a stone.

Cooling Off
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are introduced to challenges of maintaining temperatures while living in space.

That Sinking Feeling
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners observe how salinity and temperature affect the density of water, to better understand the Great Ocean Conveyor.

What's So Special about Water: Solubility and Density
Source Institutions
In this activity about water solubility and density, learners use critical thinking skills to determine why water can dissolve some things and not others.
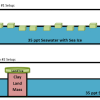
Causes and Effects of Melting Ice
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the concept of density-driven currents (thermohaline circulation) and how these currents are affected by climate change.
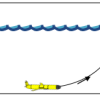
Exploring the Ocean with Robots
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are introduced to robotic submarines called gliders. Learners make “gliders” from plastic syringes and compare these to Cartesian bottles and plastic bubbles.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Toasty Wind
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners use a toaster to investigate the source for the Earth's wind. Learners hold a pinwheel above a toaster to discover that rising heat causes wind.

Uplifting Force: Buoyancy & Density
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners explore the force known as buoyancy by placing various objects into water and observing how they behave (for example, which sink more quickly, which float, how much wat
