Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 76

Give and Take
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore liquid crystals, light and temperature. Using a postcard made of temperature-sensitive liquid crystal material, learners monitor temperature changes.

Shadow Puppets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will create their own simple shadow puppets, and experiment with light and shadow while playing with them.

Kaleidoscope
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the reflective properties of light and mirrors as they make a kaleidoscope.
Stretch the Chain and See the Light
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use their strength to light a light bulb. A chain made from paper clips is placed in series with a battery and flashlight bulb.
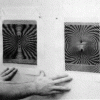
Moiré Patterns
Source Institutions
In this activity about light and perception, learners create and observe moire patterns.
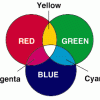
The Primary Colors of Light
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups of four to explore light. Learners create new colors from the primary colors of light from flashlights covered in theatrical gels or cellophane.

Polarized Light Mosaic
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use transparent tape and polarizing material to create and project beautifully colored patterns reminiscent of abstract or geometric stained glass windows--no glass required

Polarized Sunglasses
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how polarizing sunglasses can help diminish road glare.
Rainbow in the Room
Source Institutions
This activity generates learner excitement about light through the creation of a room-sized rainbow.

Pringles Pinhole Camera
Source Institutions
An ordinary camera has a lens that makes an image on film. In a pinhole camera, a small hole replaces the lens.

Light Maze
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore light with reflective surfaces. Learners will make predictions and share their observations as they experiment with directing a beam of light.

Seeing Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
This activity (aka "snack") provides instructions for discovering your blind spot. It is an exploration of light and visual perception using simple materials you may have around the house.

Pixel Tube
Source Institutions
In this STEAM activity, learners create a "pixel tube" to explore reflections of light and color mixing.

Convection Current
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own heat waves in an aquarium.

Up Periscope!
Source Institutions
This activity provides instructions for building a mirrored tube--a smaller and simpler version of a submarine's periscope--that lets you see around corners and over walls.

Bubble Suspension
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe as soap bubbles float on a cushion of carbon dioxide gas. Learners blow bubbles into an aquarium filled with a slab of dry ice.

On the Fringe (formerly Bridge Light)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners trap a thin layer of air between two pieces of Plexiglas to produce rainbow-colored interference patterns.

Corner Reflector
Source Institutions
In this optics/mathematics activity, learners use two hinged mirrors to create a kaleidoscope that shows multiple images of an object.
How does the Atmosphere keep the Earth Warmer?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate the energy transfer between the earth and space by using the light from a desk lamp desk lamp with an incandescent bulb and a stack of glass plates.

Turbidity
Source Institutions
This is an activity about turbidity, or the amount of sediment suspended in water.
