Search Results
Showing results 1 to 15 of 15

Identifying Erosion
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity (page 3 of the PDF), leaners will identify and explain the causes of erosion.

Do Your Own Dig
Source Institutions
In this outdoor archaeology activity, learners use mathematical skills and scientific inquiry to generate and process information from their own excavation site.

Composting
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity, learners research what is essential for plant life and the necessary components of soil to support plants.

Lilliputian Landscaping
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners examine the different materials gardeners add to their soil, and discuss how these materials are important for plant growth.
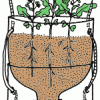
TerrAqua Investigation Column: What is the Land-Water Connection?
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners plant seeds in a 2-liter bottle filled with soil that is connected to a water source below. Over the next few weeks, learners observe how the plants grow.

How Fast Can a Carrot Rot?
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to determine conditions that either help or hinder the decomposition of carrots by soil microbes.

Super Soil
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners make their own organic-rich soil. Depending on where this activity is done, learners will probably discover that their local soil is low in organic matter.

Single-Cell Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a soil and water model of a single-cell life environment and study living microorganisms.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Runaway Runoff
Source Institutions
When it rains, water can collect on top of and seep into the ground. Water can also run downhill, carrying soil and pollution with it.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

From the Ground Up
Source Institutions
In this plant science activity, learners conduct four experiments to observe how plants respond to sunlight and gravity.

Water "Digs" It!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate soil erosion. Learners set up a simulation to observe how water can change the land and move nutrients from one place to another.

Creating a Soil Map
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate soil conditions by creating a soil map. Learners record soil characteristics and compare the conditions of soil in different grid sections.

Investigating the Uses of Backyard Bacteria
Source Institutions
The purpose of this lab is to recognize that the answers to some of society's industrial challenges may lie right in our own backyards.
