Search Results
Showing results 61 to 80 of 130
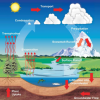
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

Toasty Wind
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners use a toaster to investigate the source for the Earth's wind. Learners hold a pinwheel above a toaster to discover that rising heat causes wind.

Transit Tracks
Source Institutions
In this space science activity, learners explore transits and the conditions when a transit may be seen.

Eclipse: How can the little Moon hide the giant Sun?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how distance can affect the way we perceive the size of an object.

Exploration Vehicles
Source Institutions
Using recycled materials, learners will design a transportation vehicle to carry an egg in an egg toss (a rudimentary model of a shock absorbent transport vessel).

Bernoulli Levitator
Source Institutions
Demonstrate the Bernoulli Principle using simple materials on a small or large scale.

Small Habitats
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a model of a self-sustaining habitat (growing grass and beans from seeds).

Weathering and Erosion
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 13 of the PDF), learners discover how weathering and erosion change the Earth’s surface.
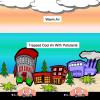
Turning the Air Upside Down: Convection Current Model
Learners see convection currents in action in this highly visual demonstration. Sealed bags of colored hot or cold water are immersed in tanks of water.

Differing Densities: Fresh and Salt Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners visualize the differences in water density and relate this to the potential consequences of increased glacial melting.

I Can't Take the Pressure!
Learners develop an understanding of air pressure in two different activities.

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Heating and Cooling
Source Institutions
Learners investigate how the temperature of water affects its density.
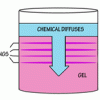
Liesegang Rings
Source Institutions
This display shows slow chemical reactions in colorful crystal formations known as Liesegang Rings. These reactions are similar to those forming the rings in agates.
Windmills
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 8-9 of the PDF), learners will explore wind energy. They will build their own windmill and see how energy from wind can be converted into a useable form.

Water on the Move: Wind and Waves
Source Institutions
In this simple activity, learners explore ocean waves. To find out if water moves forward toward the shore, learners create waves in a simulated ocean (small aquarium tank of water).

Balloon Kebabs
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners observe the effects of density and pressure by attempting to make "balloon kebabs." Learners will try to insert a wooden skewer all the way through an inflated balloon

Soda Pop Cave
Source Institutions
In this geology activity (page 6 of the PDF), learners explore how carbonic acid can slowly dissolve limestone and form caves.
Finding the Carbon in Sugar
Source Institutions
In this activity about combustion and energy, learners observe a burning candle in a sealed jar and the burning of white sugar.

Turning the Air Upside Down: Warm Air is Less Dense than Cool Air
Learners cover a bottle with a balloon. When they immerse the bottle in warm water, the balloon inflates. When they immerse the bottle in a bowl of ice, the balloon deflates.

Water, Water Everywhere
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners estimate how much water they think can be found in various locations on the Earth in all its states (solid, liquid, and gas) to discover the different water ratios in the Ea
