Search Results
Showing results 41 to 60 of 128

Cook with a Solar Oven
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own solar oven to bake s'mores and learn about how solar energy is absorbed on Earth.
The Return of El Nino
Source Institutions
In this activity related to climate change and data analysis, learners examine temperature and precipitation data to determine if climate variations are due to El Niño.
Any Year Calendars
Source Institutions
This PDF contains 12 calendars (12 months). Each month contains activities about math. Things to do on familiar holidays (like July 4), less common holidays (like Backward Day), and any day.

Freezing Lakes
Source Institutions
In some parts of the world, lakes freeze during winter. In this activity learners will explore water’s unique properties of freezing and melting, and how these relate to density and temperature.

Detect Solar Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build their own magnetometer using an empty soda bottle, magnets, laser pointer, and household objects.

Scale Model of Sun and Earth
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the relative size of the Sun and Earth as well as the distance between them.

The Ins and Outs of Tides: Learn About Causes and Predictions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will compare predicted and observed tides using data from The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration(NOAA).

The Shadow Knows II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of a shadow and use the distance from the equator to calculate the circumference of the earth.
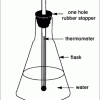
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Why Does the Moon Have Phases?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a simple 3D model to discover why the Moon has phases.

Window Under Water
Source Institutions
Glare from the sun and ripples from the wind can make it hard to see what's below the surface of a body of water.

Breaking the Code: Mayan Math
Source Institutions
This is a lesson plan for an activity in which learners, playing the role of archeologists, use math concepts about number bases to decipher the Dresden Codex, an ancient Mayan document.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.
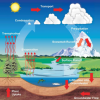
Weather Stations: Phase Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the water cycle in action! Water vapor in a tumbler condenses on chilled aluminum foil — producing the liquid form of water familiar to us as rain and dew.

Make a Terrarium
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a miniature greenhouse or "terrarium" to explore the greenhouse effect.
Effects of Solar Radiation on Land and Sea
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the different heating properties of soil and water.

Make Your Own Petroglyph
Source Institutions
In ancient Chaco Canyon, the people used a "sun dagger" petroglyph to mark the passing of seasons.

Eclipse: How can the little Moon hide the giant Sun?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how distance can affect the way we perceive the size of an object.

Exploring Earth: Paper Mountains
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore in what ways the shape of the land and the pull of gravity influence how water moves over Earth.
How does the Atmosphere keep the Earth Warmer?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate the energy transfer between the earth and space by using the light from a desk lamp desk lamp with an incandescent bulb and a stack of glass plates.
